C++ Programming
Q1.What is C/C++?
Ans.

C++ is an object oriented programming language.It is known as mother of all programming languagesbecause it sets strong base for fundamental programming approach. This approach almost can be applicable to all programming language. It is a powerful Language.
It can be used to develop operating systems, browsers, games, network programming , graphic shapes etc. C++ supports different ways of programming like procedural, object-oriented, functional, and so on. This makes C++ a must to learn programming language.
Q2.Who invented c++?
C++ is invented by BJourne Strous Stroop.
Q3.when c++ was invented ?
Ans c++ was invented in 1979.
Q4.Why c++ or what are the feature that makes it so popular?
Ans
The feature that makes it strong among all programming
language are as follows :-
1.It is simple to learn.
2.It is procedural / Oops Based both.
3.It is machine dependent.
4.it is easy and fast.
5.It is interactive means it can used to make graphicalshapes and add movements to them, that makes it interactive .
6. It is associative . means the program made in c++can be associated or embedded or included in pl likejava, android,python.
7.C++ supersedes C as it has all the features of C i.e.is c++ = c+oops.
8.It can be used in handling hardware devices as it uses pointers, that can directly access memory address for reading / writingof data.
9. c++ views eveything in the form of an object that makes handling programming easier.
10.c++ is very powerful. because it has a powerful set of library with many functions
Micro Controller or Micro Processor ?
a microcontoller (µC) contains not only processing unit but small amount of memory (ROM, RAM etc.), few IO ports for peripherals, timer etc. We can think of microcontoller as a mini computer. microcontoller can be called a SoC (System on Chip) that is built typically for embedded system use.use of µC in home appliances such as Washing Machine, Ovens etc. Ex. Examples of µC are ARM(Advance RISC Machine) Cortex-M series, Intel 8051 etc.
a microprocessor (µP) contains only processing unit which is quite powerful in terms of computing. To make use of microprocessor (µP), one needs extra hardware chips such as memory (RAM), peripheral boards, system bus etc. It means that µP cannot be used stand alone. Examples of µP are ARM Cortex-A series, Intel Pentium series etc. we can find the use of µP in desktop computers, laptops etc.
If someone is devising an embedded system where specific and customized tasks need to be done, picking µC is a typical choice. On the contrary, if someone is devising a general purpose computing device, picking µP is a typical choice.
Q5.What is an object?
Ans An object is thing that has some characterstrics, state and behaviour.
example :
pen,chair,fan, halicopter,computer , laptop,mobile , glider etc. .......
Q6. What are the rules for c++ Programming?
Ans.
1. C++ is case sensitive
2. c++ has only one main function main()
3. c++ usesturboc++ compiler for making its program and
other compiler code blocks, developer c++ , vs code.
4. each c++ statement is terminated by ; (semicolon)
5. c++ statement kept in block { } are understood as group
statements.
5. c++ comments are written as
// - single line comments
Multiline comments can be give by :
/* ......
*/
6. c++ uses access specifiers for setting accessibilityof data members and function.
7.c++ uses #sign which is known as pre processor directiveit is used to include header files which are having function to work with various perpheral and for other purposes.
#include< headerfile >
8.To interact with os c++ uses command line arguments.
9.each c++ program has a return statement it is must incase the main() is returning some values otherwise itcan be ignored.
.......
Q7.What are header files?
Ans.
Header files are library files that contains functionsthat are already compiled and tested so can be used directlyin the program and can run without errors and saves timein project development.
Q7a What is the use of Namespace ?
Ans.Consider you are writing a code that has a function named as xyz() and there is another library available which is also having the same function named xyz(). Now the compiler will be confused with the function you are referring to within your code.
Namespace has been designed to overcome this difficulty. Using namespace, you can define the context in which the name is defined.C++ consists of a standard namespace, i.e., std which contains inbuilt classes and functions. So, by using the statement "using namespace std;", the compiler includes the namespace "std" in our program.
Q8a.What is a compiler?
Ans A compiler is a program that compiles / convertes a program
into a binary language that a computer can understand .
The compiler compiles the whole program and display error if
any at the time of compiling.
Q8b.What is an Interpretor?
Ans AnInterpretor is a program that convertes a programinto a binary language that a computer can understand . The compiler compiles the whole program and display error ifany at the time of compiling.
Q9. What are tokens ?
Ans Tokens are basic or smallest units of programming .
These are :-
1.Alphbets
2.Numbers
3.Symbols
4.Escape Sequence
5.Literals
6.Keywords
7.Identifiers
1. Alphabets
a. character : A-Z or a-z
digits : 0 -9
symbols : ;,',"",<>,~,% &, {},(),/,//....
b.Number System /Digits : 0 -9
decimal number system : 0-9
binary number system 0-1
octal number system : 0-7
Hexa decimal number 0-15 ( 0-9,A,B,C,D....F)
Ox7273A5E
Decimal Binary
0000 0000
1 0001
+ 1
2 0010
3 1
0011
4 +1
0100
5 +1
6 0101
8 1000
Convert numbers from decimal to binary
0 0000
1 0001
+1
2 0010
3 +1 = 0011
1A. Literals : Literals are the constants used to assign values to variables.
Num =1,grade = ‘A’ amount =299.90;
2.Keywords
Keywords are the reserved words that conveys special meaning to compiler.
These keywords are :-
if,else,for,while , do-while,class, return , structure, union, int,char ,float
double, break , continue, goto etc.
3.Data type
10.What are data type ?
Ans .
Data type are the reserve words that are used to declaredata members and other variable and used to identify the type of data that a variable can hold.
These are of two types of data types :
1. Premitive data type
These are the orginal data type and not inherited from any where means are
the basic units.
Sno. Data type Size Ranges
1. char 1 byte -128 to 127
2. int 2 byte -32768 to 32767
3. Float 4 byte
4. Double 8 byte
1 byte = 8 bits
bits are combination of 0 and 1s
1kb = 1024 byte
1mb = 1024 kb
1gb =1024 mb
1tb =1024 gb
2.Secodary Data types
These are the data type that are known as user defined data type
or are made up of basic data types. ex. class,array , enum .
3. Identifiers
Identifiers are the words that are defined for the purposesof nam
Q10a.What are variables?
Variables are the names given to memory locations that areused to store data temporarily.
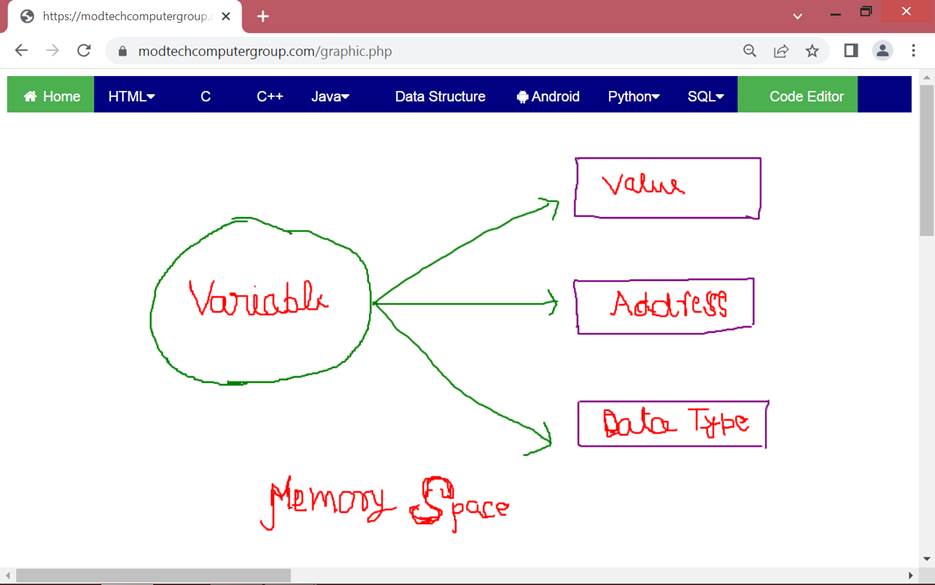
Q11.How to declare a variable?
ans.
syntax :
<type > name ;
exmample
int age;
char grade;
float amount;
double macronNo;
age =10;
grade=’C’;
amount = 10.50;
Q12 How to write c++ first program?
Ans.
1. In turboc C++
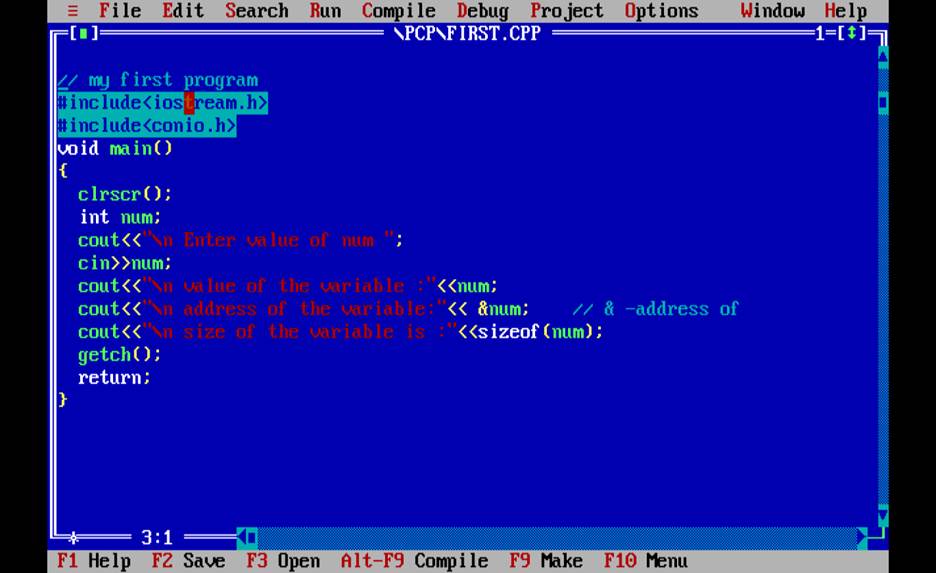
//2.my first c++ program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
Clrscr();
int num;
num=10;
cout<<"\n value of variable is :"<<num;
cout<<"\n address of the variable is :"<<# // address
cout<<"\n Size of the variable is :"<<sizeof(num);
cout<<"press any key to see output";
getch();
return;
}
Q13 How to write c++ program by user input?
Ans.
// my first c++ program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int num; //declaration
cout<<"\n Enter a number :";
cin>>num;
cout<<"\n value of variable is :"<<num;
cout<<"\n address of the variable is :"<<# // address
cout<<"\n Size of the variable is :"<<sizeof(num);
cout<<"press any key ....";
getch();
return;
}
Q13. What is Typecasting ?
Ans. Converting one type of data to another type is known as type-casting.
It can be of two types :-
1.Implitcit Typecasting
2.Explicit Typecasting
1.Implicity Type Casting
It is automatically being converted to another type of data is known as implicit typecasting.
//A-Z 65-90
//a-z 97-122
Int a =68;
char ch;
Ch = a; //implicit
cout<<”\ n value of ch is :”<< ch;
output : D
//write a program to print alphabets ?
Ans.
// printing alphabets
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int num;
cout<<”\n enter a number’s ASCII :”;
cin>>num;
char ch=num; // implicit
cout<<”\n alphabet for the given number :”<<ch;
getch();
return;
}
2.Explicit Type Casting
It is done by explicitly defining the type of data then conversion takes place accordingly .
Float amt = 200.60;
Int net;
net = (int)amt;//explicit
cout<<”\n value of net is :”<<net; //200
Q14.What are the operators?
Operators are used to perform various kind of operations inthe computer. These operators are :-
1.Arithmatical operators +,-,*,/,%(modulus)
2.Comparision Operators >< ==
3.Relational Operators>= <= <> !=
4.Logical Operators &&,|| !
5.Bitwise operators& | !
6.Ternary Operators ?:
7.Unary Operators ++, --
1.Arithmatical operators
// wap to find sum of two numbers
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a, b,s=0; //declartion
a=10;
b=20;
s=a+b;
cout<<”\n sum of two numbers is :”<<s;
getch();
return;
}
// wap to find sum of two numbers by user input
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a, b,s=0; //declartion
cout<<”\n enter value of a :”;
cin>>a;
cout<<”\n Enter value of b :”;
cin>>b;
s=a+b;
cout<<”\n sum of two numbers is :”<<s;
getch();
return;
}
// Arithmatical Operators
//program to check whether a given year is leap year.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int myear;
cout<<”\n Enter a year to check :”;
cin>>myear;
//myear = 2012;
if ( myear%4 ==0 )
cout<<" this is a leap year ";
else
cout<<" not a leap year ";
getch();
return 0;
}
Q15.Wap to check whether a given number is odd or even
// Arithmatical Operators
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int num;
cout<<"\n Enter a number :";
cin>>num;
if ( num%2 ==0 )
cout<<" the is a even number ";
else
cout<<" is odd number ";
getch();
return 0;
}
Comparision Operator >< == <> !=
These are the operators that are used to compare two or more
expressions
example
// comparision Operators
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b;
a=10;
b=20;
if ( a>b )
cout<<”\n a is greater “;
else
cout<”\n b is greater or equal ";
getch();
return 0;
}
Relational Operator >= <= == <> !=
These the operators that are used to compare and set relation
between two or more expressions
example
// RelationalOperators
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
a=10;
b=20;
if ( a>=b )
cout<<"\n a is greater or equal";
else+
cout<<"b is greater";
getch();
return;
}
Logical Operator && - And || -or ! not
Logical operators are used to combine two or more expressions.
and then it returns ‘true’ or ‘false’ value which is a logical value.
example
// Logical Operators
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int marks;
char grade;
cout<<"\n Enter your marks :";
cin>>marks;
if ( marks>=33 && marks<45 )
grade ='D';
else
if ( marks>=45 && marks<60 )
grade ='C';
else
if ( marks>=60 && marks<75 )
grade ='B';
else
if ( marks>=75 )
grade ='A';
else
grade ='F';
Cout<<"\nYour marks are and your grade is "<<marks <<” “<<grade;
getch();
return;
}
Q16.Wap to find the the designation of an employee on the basis of salary being paid to him.
a. If salary is greater than 20000 and less then 40000 design “Clerk”
b. If salary is greater than or equlal 40000 and less then 60000 design “Ass officer”
c. If salary is greater than or equal 60000 and less then 80000 design “Officer”
d. If salary is greater than or equal 80000 and less then 100000 design “Manager”
e. If salary is less than 20000 is “ no desgin”
Bitwise Operator & and | or ! not
These are used to test the devices input /output, actually these are used in logic gates and gates are thecircuits those take input and out in 0 and 1.
TT (Truth Table )
X Y AND* OR + ! NAND NOR ………
0 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 1 0
Q wap to multiply two numbers using bitwise operators
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// declare variables
int a = 12, b = 25; //12=00001100 25 = 00011001
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "a & b = " << (a & b) << endl;
return 0;
}
output:8 00001000
Q Wap to convert a decimal number into binary ?
ans. divide decimal number by 2 until remainder becomes 1 or 0
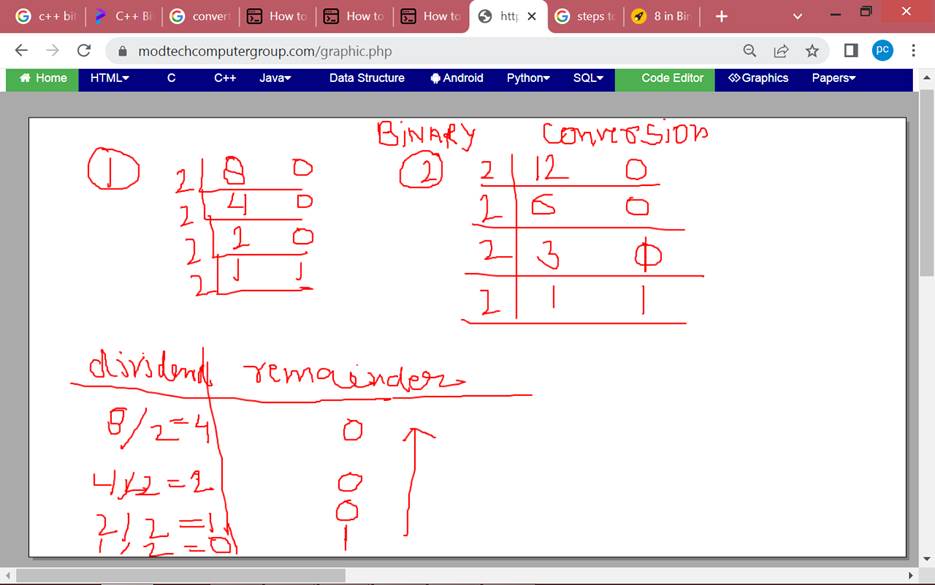
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int decimal, binary = 0, remainder, product = 1;
cin >> decimal;
while (decimal != 0) {
remainder = decimal % 2;
binary = binary + (remainder * product);
decimal = decimal / 2;
product *= 10;
}
cout << "The number in the binary form is: " << binary ;
return 0;
}
Q17.Wap to show wether the device (inverter) is producing output and panel is being tested.?
// bitwise Operators
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int signal;
int light = 1;
cout<<"Enter your device signal ";
cin>>signal;
if ( light & signal )
printf("\n invertor is off : light is due to direcly supply");
else
printf("\n invertor is on : light is from inverter");
getch();
return;
}
//C++ program to count total of zeros and ones in a binary number using bitwise //operator
#include <stdio.h>
#define INT_SIZE sizeof(int) * 8 /* Total number of bits in integer */
intmain()
{
int num, zeros, ones, i;
/* Input number from user */
cout<<"Enter any number: ";
cin>>num;
zeros = 0;
ones = 0;
for(i=0; i<INT_SIZE; i++)
{
if(num &1)
ones++;
else
zeros++;
num >>= 1;
}
Cout<<"Total zero bit is :” <<zeros;
Cout<<"Total one bit is :”<<ones;
return0;
}
Ternary Operator ( ? : )
This operators is used to test an exp. and return value.
// Ternary Operators
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int marks =70;
char result;
result = marks>=33 ? 'P' : 'F';
cout<<"Your marks are and your result is p-Pas f-fail ",
marks,result);
cout<<”\n your marks are “<< marks <<” Result “<< result;
return;
}
Q18.Wap to print the eligibility of a voter to vote by getting user’s input ?
Ans.
//voter’s eligibility
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
Clrscr();
Int age;
Char eligiblestatus;
cout<<”\n enter voter’s age :”;
cin >> age;
eligiblestatus = age>=18 ? ‘E’ : ‘N’;
cout<<”\n your are e-eligible n-not eligible for voting :”<<eligibilestatus;
getch();
return;
}
Unary Operator ( only one operand )
These are used with an operand and used to increment and decrement
value of the operand.
a a=a+1 a++ (post fix ) ++a (pre fix )
++a - add first then print or use me
a++ - use me or print first then add
//wap to find the value of an operand?
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a =10;
cout<<”value of a is :”<<++a;
cout<<”\n Value of a is :”<<a;
getch();
return;
}
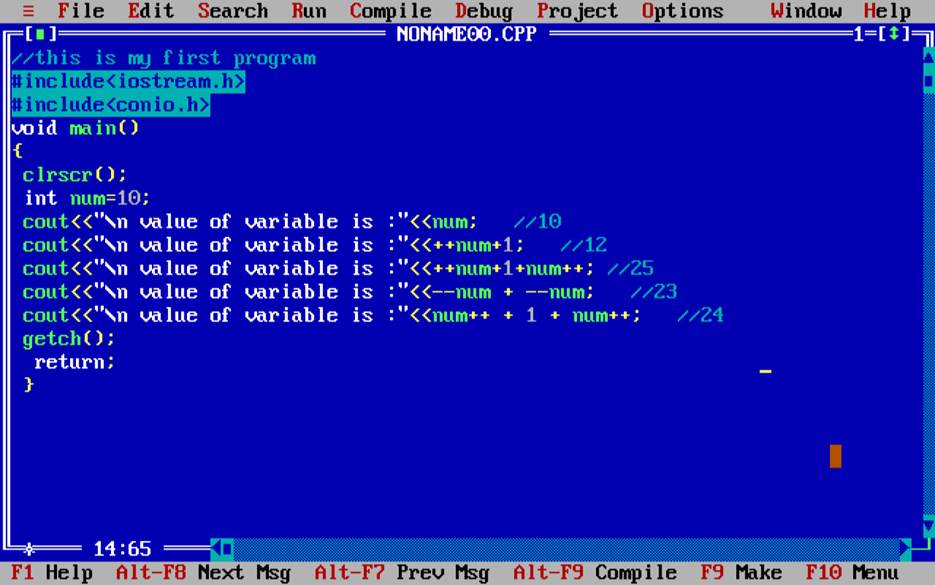
Ex2.
//file value of num...
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int num=10;
cout<<"\n value of num is :"<< --num + 1 + num--;
cout<<"\nvalue of num :"<<num+ --num;
getch();
return;
}
Ans is … ? explain ..?
Int num =10;
Cout<< num++ + --num+1
Q18.What are Conditional Construct/statements ?
These statements are used to test a condition and on that basis it will execute the statement.
These are :
1.if ..else
2.switch statement.
Switch Statement
This is used to test an expression and displays multi branching or various cases to perform on the basis of expression result.
Syntax :
Switch( exp )
{
Case 1 :
{
Statement1;
Statement2 ;
break;
}
Case 2 :
{
Statement1;
Statement2 ;
Break;
}
Case 3 :
{
Statement1;
Statement2 ;
Break;
}
default :
{
Statement1;
Statement2 ;
Statement3;
Break;
}
}
Q18.What is Looping ?
Ans.Looping is process in which a task is performedfor a number of times.Looping in c++ is permormed by the following:
1.for---Loop
2.While Loop
3.do while ..Loop
For –Loop
This loop should be used when the looping process (repetition ) is fixed or known.
Syntax :
For( initialization;condition;counter)
Example
Q1. Wap to print first 10 natural numbers?
Ans.
//my program for printing 10 numbers
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
for( int i=1;i<=10;i++)
cout<<”\n”<<i; //cout<<i<<endl;
getch();
return;
}
Outpu : 1,2,3,4…..
Q2.Wap to print first 100 numbers in reverse order
//my program for printing 10 numbers
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
for( int i=100;i>=1;i--)
cout<<”\n”<<i;
getch();
return;
}
Nested Loop
A loop inside another loop is known as nestedLoop.
Ans.
Syntax:
For( initializataion;condition;counter)
{
For( initializataion;condition;counter)
{
// body of inner loop
}
}
Ex.Test how many times the inner loop is rotating on one time rotation of out loop.
// nested loop
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Int j;
For( int i=1;i<=5;i++) //outer
{
For(j=1;j<=5;j++) //inner
{
Cout<<”outer value of I is “<<i<<”Inner value of j is :”<<j;
Cout<<”\n”;
} }
getch();
return;
}
Output :
Outer 1 inner 1
1 2
1 3
Q3.Wap to print tables from 1 to 10
Ans.
// printing table
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<dos.h>
Void main()
{
Clrscr();
Int I ,j;
Sound(100); 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9
For ( I =1;i<=10;i++) 2 4 6 8 10 12 16
{ 3 6 9 12
Delay(70);
Sound(150);
For( j=1;j<10;j++)
Cout<<i*j<<”\t”;
Cout<<”\n”;
}
Nosound();
Getch();
Return;
}
Q4.Wap to print the following using nested loop
//printing patterns
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
//Using namespace std;
Void main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=0 ; i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=i;j++)
cout<<”*”;
cout<<”\n”;
}
getch();
return;
}
A
*
**
***
****
*****
b.*****
****
***
**
*
c.
1
12
123
1234
12345
d.
7
77
777
7777
77777
f.
*
* * *
* * * * *
* * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * *
Q10.WAP to print the followingpyramid ?
//my pattern printing
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<dos.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int rows,i,j,k;
int space;
rows=20;
cout<<"\n Enter no. of rows in the pattern";cin>>rows;
for( i = 1;i<=rows;++i)
{
sound(i*100);
delay(65);
for(j=1;j<=rows-i;++j)
{
sound(j*150);
delay(30);
cout<<"";
}
for(k=0; k != 2*i-1 ; ++k)
{
sound(k*80);
delay(55);
cout<<"* ";
}
cout<<"\n";
k=0;
}
nosound();
cout<<"\n Press a key.....";
getch();
return;
}
Q2 Write a program to check whether a given number is prime number ?

While Loop
This type of loop is used where the looping process is not
Fixed.
Syntax
Initialization;
While ( condition )
{
Statement1;
Statement2;
Statement3;
Counter;
}
Ex. Wap to print first 10 natural numbers.
// my while loop
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Int i =1;
While( i<=10 )
{
Cout<<i<<endl; //endl =’\n’
i++;
}
getch();
return;
}
Q1 wap to print the following 1,4,7,10,13,16,..
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
int I = 0;
While( I < =50)
{
Cout<<3*i+1<<”\t”;
I++;
}
getch();
Return;
}
Q2.print each character of the given string( Char s[10]=”sparrow”)
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Int i=0;
Char s[] =”sparrow”;
While( S[i]!=’\0’)
{
Cout<<s[i]<<endl
I++;
}
getch();
Return;
}
Do ..While Loop
This loop is executed atleast once and then the condition
Is checked.if condition is found true then the loop will be
Re-executed otherwise it will be terminated.
syntax
do
{
Statement1;
Statement2;
Statement3;
} while (condition );
Ex. Do while loop
//do while…
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
Int ans;
Do
{
Cout<<”\nMain Menu”;
Cout<<”\n=========”;
Cout<<”\n1.Samosa”;
Cout<<”\n2.Momos”;
Cout<<”\n3.Frech Fries”;
Cout<<”\n4.Pizza”;
Cout<<”\n5.Burgar”;
Cout<<”\n6.Desert”;
Cout<<”\n7.cold drink”;
Cout<<”\n8.Exit…”;
Cout<<”\n\n Enter your choice 1-8”;
cin>>ans;
Switch( ans )
{
Case 1: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for samosa”;
Break;
}
Case 2: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for momos”;
Break;
}
Case 3: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for French Fries”;
Break;
}
Case 4: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for Pizza”;
Break;
}
Case 5: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for samosa”;
Break;
}
Case 6: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for samosa”;
Break;
}
Case 7: {
Cout<<”\n You have opted for samosa”;
Break;
}
Case 8: {
Cout<<”\n you will exit of the menu”;
Break;
}
Default : {
Cout<<”invalid input”;
Break;
}
}
}while( ans !=8 );
getch();
Return;
}
Break Statement
This statement is used to transfer program control out of the switch statement from the case block.
Continue Statement
This statement transfer program control beginning of the switch for re-testing switch again.
Q2.What is recursion ?
Ans. When a function calls itself . ie.known as recursive function and the process is known recursion?
Example: finding factorial of a number .
gg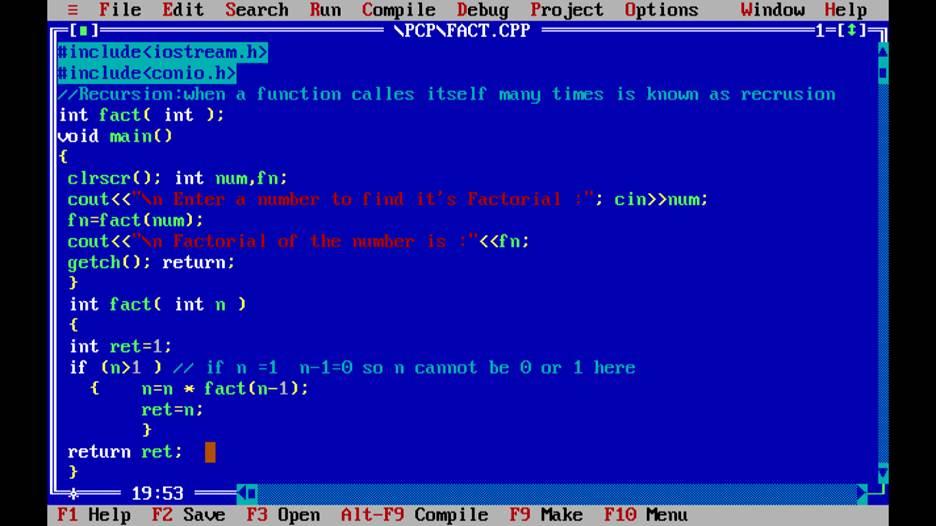
Q4.Write a program to print first 100 prime numbers

Q5.Write a program to print fabonacci Series.
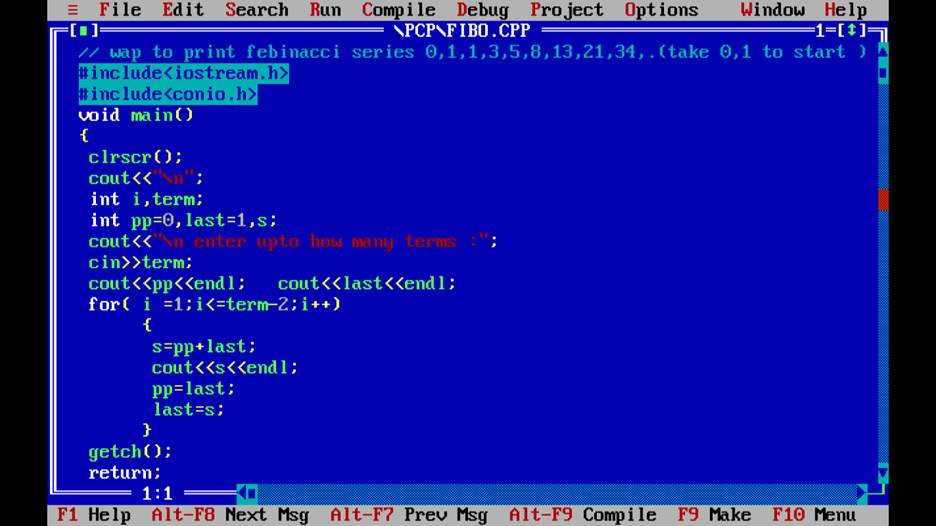
Q6.Wap to print /check whether a number is palindrome
Q7.wap to run a loop infinitly
Ans. While(1)
{
Cout<<”cpp”;
}
Or.
for( ;;)
QWAP to print no of digits in given number ?
Ans.
#include <IOSTREAM.h>
#include<conio.h>
intmain()
{
int num;
int count = 0;
cout<<"\Enter any number: ";
cin>>num;
do
{
count++;
num =num/10;
} while(num != 0);
Cout<<"Total digits:”<< count;
return0;
}
Arrays
Q1.What is an Array?
Ans.An Array is set of similar elementsOr is a character array.
Q2.What is the use of an array?
Ans.
1.Element are stored in contiguous block
2.Accessing is faster
3.Moving to next element can be done byJust increment or decrementing element Index.
4.It is reducing overheads of to and fro of Searching of an element as compared to Variables.
Q3.How to declare an array?
Ans.
Data-Type array_name[size];
Ex.
int marks[5];
Q4. How to initialize an Array?
Ans.
Int mark[5]={90,60,70,50,65};
|
Index |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value |
90 |
60 |
70 |
50 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addres in memory |
1001 |
1003 |
1005 |
1007 |
1009 |
|
|
|
|
|
Char name[7] = “Sparrow”
|
Index |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
Value |
S |
P |
A |
R |
r |
o |
W |
|
Address |
1001 |
1002 |
1003 |
1004 |
1005 |
1006 |
1007 |
Q 5. How to access array elements ?
Ans.
Int Arr[5]={15,45,85,63,47}
Arr[0] = 15
Arr[1] = 45
Arr[2] = 85
Arr[3] = 63
Arr[4] = 47
Q6.How to print an Array?
Ans.
//printing of an array
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
int arr[5]={15,45,85,63,47};
For ( int I =0;i<5;i++ )
Cout<<arr[i];
Getch();
Return;
}
Q7.Wap to print marks of a student and find his average?
//printing of an array
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Int arr[5]; //declaration
Int s=0,avg=0;
cout<<”\nEnter your marks :”;
For ( int i =0;i<5;i++ )
Cin>>arr[i];
For ( int I =0;i<5;i++ )
{
cout<<arr[i];
s=s+arr[i];
}
Avg= s/i+1;
Cout<<”\n Total marks of the student are :”<<s;
Cout<<”\n Average marks of the student are”<<avg;
Getch();
Return;
}
Q1.Wap to print frequency of a number using one dimensional array?
Ans.
Frq[] = { 7,9,7,60,10,20,1,15,1,21,8 ,7 }
Ans.
// Freq.. of a number
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Int Frq[] = { 7,9,7,60,10,20,1,15,1,21,8 ,7 }
Int fq; int cnt;
Cout<<”\n enter a number to find the frequency : “;
Cin>>fq;
Cnt=0;
For ( int I =0;i<12;i++)
If( frq[i]==fq )
Cnt++;
Cout<<”Total Frequency of the number entered is :”<<cnt
Getch();
Return;
}
Two dimensional Arrays
It has rows and columns to store values rows and columns
Combination is known cells .A two dimensional array is
Also knows as a matrix.
Columns 0 1 2
|
(0,0) |
(0,1) |
(0,2) |
|
(1,0) |
(1,1) |
(1,2) |
|
(2,0) |
(2,1) |
(2,2) |
|
45 |
89 |
90 |
|
75 |
75 |
79 |
|
58 |
35 |
55 |
Q2.Wap to print each cell value of a two dimensional matrix?
Ans.
// printing of two dimensional array
#
#
Void main()
{
Int I,j;
Int A[3][3]={ 45,89,90,
75,75,79,
58,35,55
};
|
45 |
89 |
90 |
|
75 |
75 |
79 |
|
58 |
35 |
55 |
For( i=0;i<3;i++ ) //for row
{
For( j=0;j<3;j++) // for column
{
Cout<<A[i][j];
Cout<<”\t”; //tab
}
Cout<<”\n”;
}
Getch();
Return;
}
Q3.Wap to find sum of two matrix and print in C Matrix?
Ans.
|
50 |
60 |
85 |
|
35 |
90 |
55 |
|
38 |
25 |
15 |
A B
|
45 |
89 |
90 |
|
5 |
75 |
79 |
|
58 |
35 |
55 |
C[i][j] = A[i][j]+B[i][j];
C
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
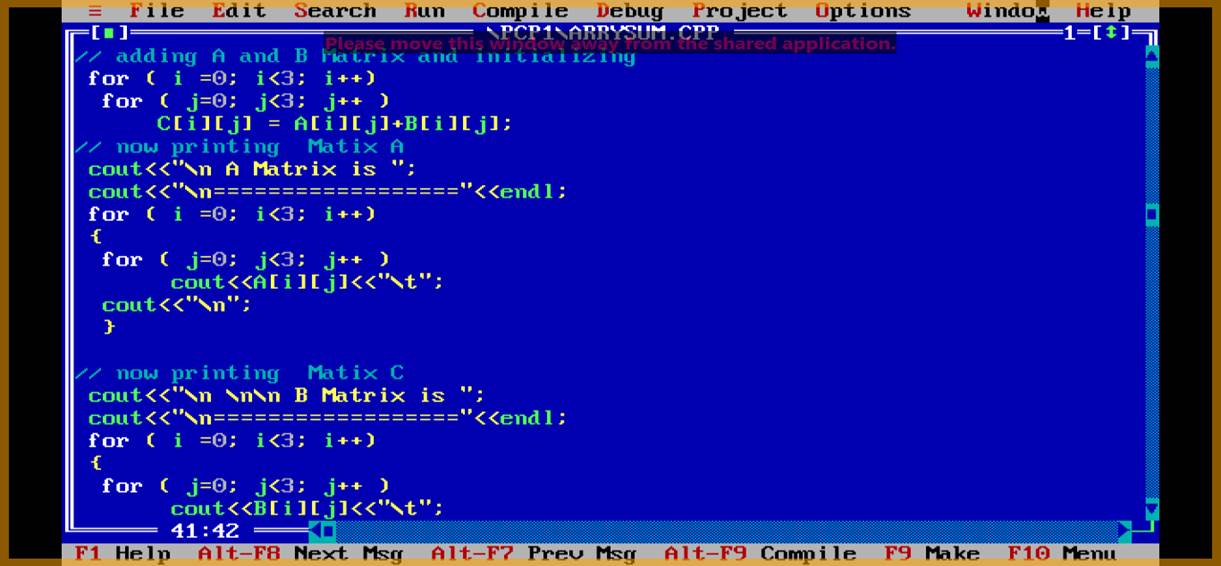
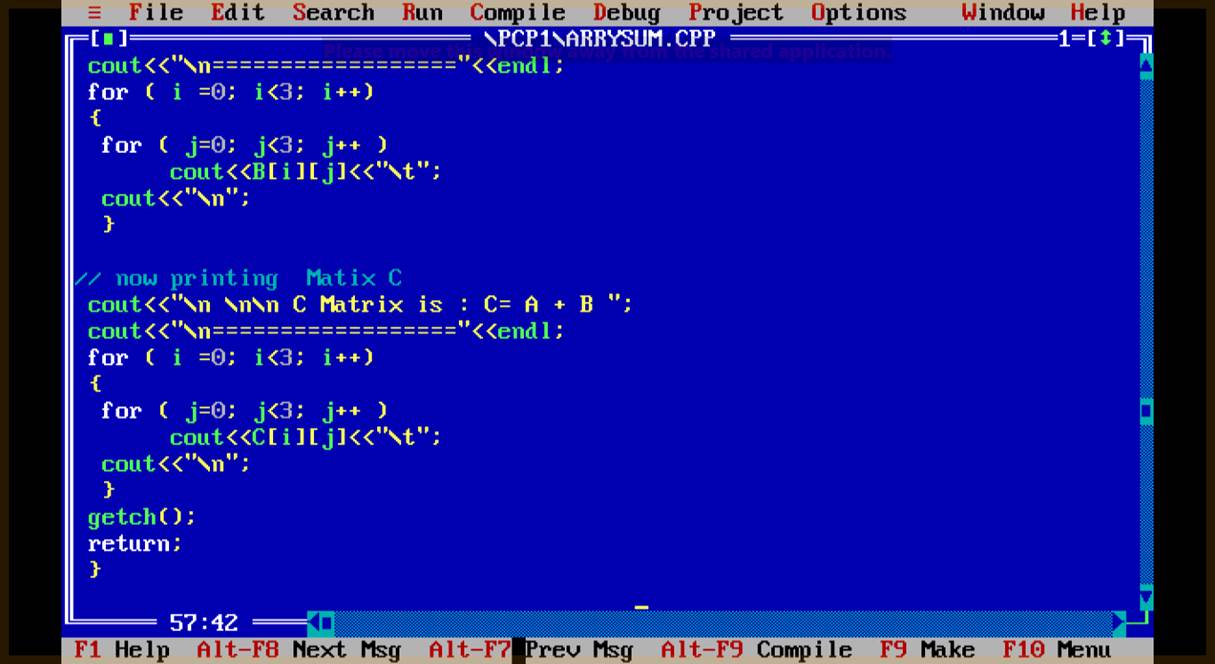
// sum of two dimention array.////
#
#
Void main()
{
Int I,j;
//print of A matrix.
Cout<<”A Matrix”
For( i=0;i<3;i++ )
{
For( j=0;j<3;j++)
Cout<<A[i][j]<<”\t”;
Cout<<”\n”;
}
//print of B matrix.
For( i=0;i<3;i++ )
{
For( j=0;j<3;j++)
Cout<<B[i][j]<<”\t”;
Cout<<”\n”;
}
//find sum of the matrix…..
For( i=0;i<3;i++ )
For( j=0;j<3;j++)
C[i][j] = A[i][j]+B[i][j];
//print of C matrix.
For( i=0;i<3;i++ )
{
For( j=0;j<3;j++)
Cout<<C[i][j]<<”\t”;
Cout<<”\n”;
}
Getch();
Return;
}
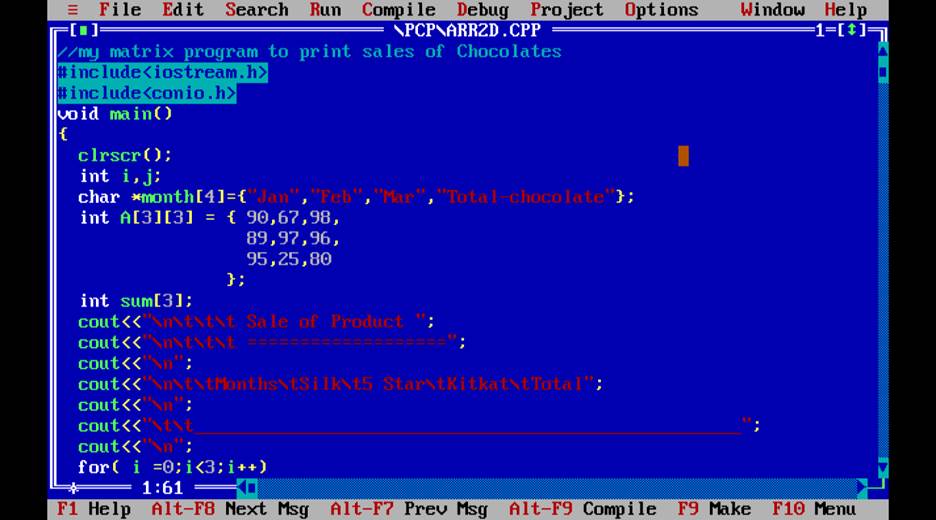
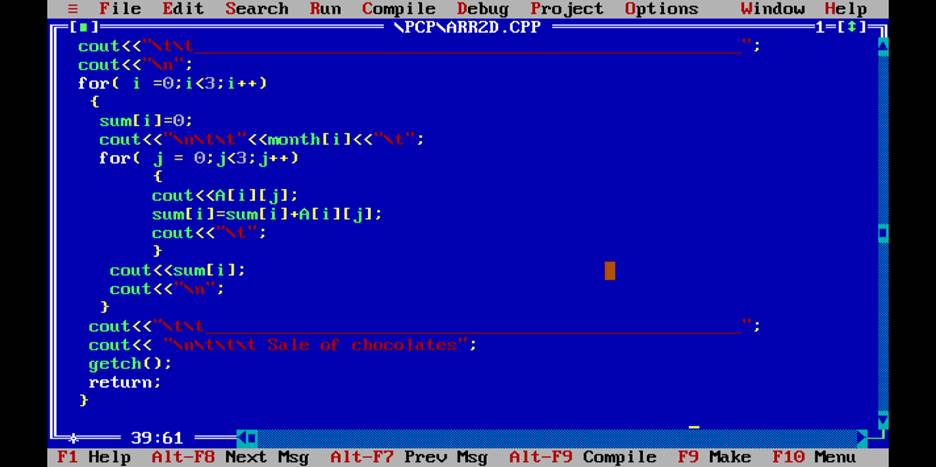
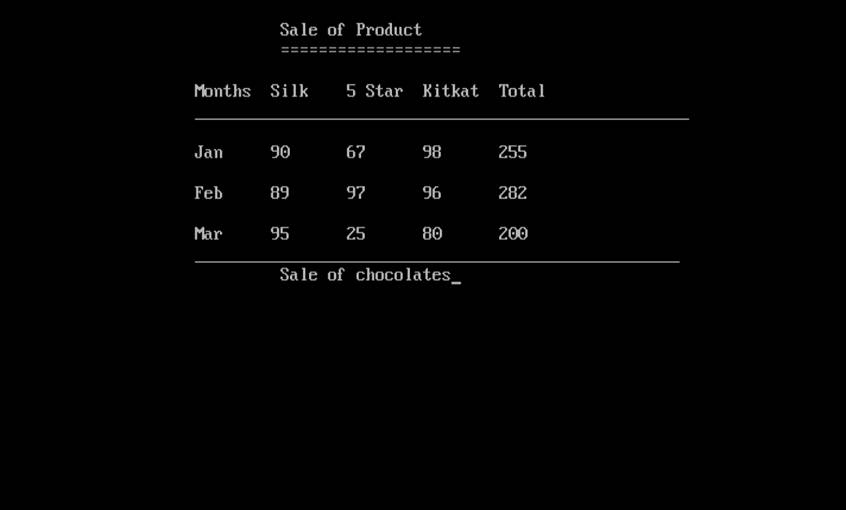
Q. Write a program to find month sale of the following product Sold ?
|
Product Name/month |
Kitkat |
5Star |
Silk |
Total |
|
Jan |
200 |
500 |
900 |
|
|
Feb |
300 |
700 |
850 |
|
|
Mar |
350 |
600 |
775 |
|
Output:
Strings
Q1.What are Strings?
Ans Strings are set of characters or are array of characters?
Q2.How to declare a string?
Ans.
char <string name >[size];
char s1[30];
Q3.How to initialize a string ?
Ans. char s1[6] = "School";
Q4.How to access string elements ?
Ans.
//
#
#
void main()
{
char s1[100]="school";
s1[0] = 'S'
s1[1] = 'c'
s1[2] = 'h'
s1[3] ='o'
s1[4]= 'o'
s1[5]= 'l'
for(int I =0; i<6;i++)
cout<<s1[i];
}
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
I |
n |
d |
i |
a |
‘\0’ |
Q5.Wap to print all character of a given array?
Ans.
// printing a string elements
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
char s[30]="india";
for(int i = 0;i<5;i++)
cout<<s[i]<<endl;
getch();
return;
}
note :
1. Each array index starts with 0.
2.each and every string ends with a character '\0' i.e. null character that shows end of the string .
3.String name or array name is itself a pointer to that array or string means its holding base address or the address of the first element of that array or string..
Q5a.Wap to find length of an user entered string ?
Ans. // string length
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s[100];
Cout<<”\n enter a String :”;
Cin>>s;
for(int i = 0;s[i]!='\0';i++)
cout<<s[i];
cout<<”\n Length of the Message :”<<i+1;
getch();
return;
}
Q6.What are the string handling functions?
Ans.
String can be handled by two ways:
1.by using inbuilt functions
2.by user defined functions
Inbuilt functions are :-
inbuilt functions are defined in the library string.h header file
1.strlen(s) - It is used to find length of the string
2.strcpy(s1,s2) - This function is used to copy one string to another
3.strcat(s1,s2) - This function is used to add two string
4.strupr(s) - converts lower case to upper
5.strlwr(s) - converts all characters in lower case
example
strlen(s)
// my string ( inbuilt functions ) to find length of a string
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s1[30]=”Sparrow is a beautiful bird”;
cout<<”\n Length of the string :”<<strlen(s1);
getch();
return;
}
strcpy(s1,s2)
// my string ( inbuilt functions )-strcpy
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s2[30]=”Sparrow ”;
char s1[30] =””;
cout<<”\n my copied string is :”<<strcpy(s1,s2);
getch();
return;
}
Q.Wap to copy a received message to mystring in my folder for view ?
strcat(s1,s2)
// my string ( inbuilt functions )-strcat
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s1[30]=”Sparrow”;
char s2[30] =”is a beautiful bird”
cout<<”\n my concatenated string is :”<<strcat(s1,s2);
getch();
return;
}
Q7. Wap to add the given stringsto make a sentence?
fields are : s1=”The” s2=”sun” s3=”is” s4=”bright”
Ans.
//hint : strcat(strcat(strcat((s1,s2),s3),s4))
Q8.Wap to illustrate use of all inbuilt functions in program ?
// string
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
Void main()
{
char s[30]="parrot";
char s1[30]="";
char s2[30]="sparrow";
cout<<"\n string length is :"<<strlen(s);
cout<<"\n string in uppercase :"<<strupr(s);
cout<<"\n string in lowercase :"<<strlwr(s);
cout<<"\n the copied string is :"<<strcpy(s1,s2);
cout<<"\n the concatenated string is :"<<strcat(s,s2);
getch();
return;
}
Q9.Wap to accept from user fname,middle and last name of a voter and place them in name string and display it.
Q10.you have two servers with thirteen digit as their address string. Server1, server2 . Now you have to exchange them?
Ans.
server1 ="192.898.101.13"
server2=”191.233.144.16”
Q11.How to make multiple copies of a string?
Ans.
// messages copying………..
#include<iostream.h>
#Include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
Void main()
{
Char msg1[250]=”Once upon a time there lived a sparrow with her husband on a tree. She had built a nice nest and laid her eggs in the nest. One morning, a wild elephant with spring fever feeling restive came to the tree in search of shade and in a rage broke the branch of the tree on which the nest was residing.”;
Char msg2[250];
Char msg3[250];
Char msg4[250];
Strcpy(msg2,msg1)
Strcpy(msg3,msg1)
Strcpy(msg4,msg1)
Cout<<”\n given msg is :”<<msg1;
Cout<<”\n msg2 is :”<<msg2;
Cout<<”\n msg3 is :”<<msg3;
Cout<<”\n msg4 is :”<<msg4;
Getch();
Return;
}
Q.Write a program to submit a practical lab report that is being completed in a group of four students for final submission in one page
Ans.
Char s1[100]=”\nmy lab testing of this chemical is red . ”;
Char s2[100]=” \nmy lab testing of this chemical is white.. ”;
Char s3[100]=” \nmy lab testing of this chemical is smoky. ”;
Char s4[100]=” \nmy lab testing of this chemical is color lime calcium carbonate…. ”;
Char s5[100];
Cout<<strcat(s5,(strcat(s1,strcat(s2,strcat(s3,s4)))));
Q.wap to get one paragram from user and print it as one character upper and another charater lower of the paragraph. ?
Q10.What are user defined functions?
Ans.
Functions that are being created and declared by user are
known as user defined function.
Functions
Q1. What are functions?
Functions are program or subroutines that are made for specificpurpose and they return some value;
Q2.What is the use functions?
ans .
Function has the following benefits :-
1.They reduces development time.
2. They improve readability.
3. They runs faster.
4.They are re-useable, Reusability means functions can be used again and again.
5. Error handling or repairing will become easier.
Q3. What are the parts of a functions ?
ans.
1.Prototype - These are the rules that are to be followed
while defining function.
int VehicleOnRoad(int Left, int right);
Return_type func_name( int, int ….);
2.Function calling - function can be called by the following syntax
var=func_name( arg1,arg2..)
3.Function definition
This is the function body that defines how the function works.
Return type func_name( int arg1, int arg2…)
{
//code here
}
example:
Q 4.Wap to find the number of vehicles running on road at a particular moment of time?
Ans.
//vehicle count
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Int VehicleOnRoad(int , int); //prototype
void main()
{
int total_count;
int left,right;
cout<<”\n No. of vehicles moving on left side road :”;
cin>>left;
cout<<”\n No. of vehicles moving on right side road :”;
cin>>right;
total_count = VehicleOnRoad(left,right); //calling
cout<<”\n Total no. of vehicles “<<total_count;
getch();
return;
}
Int VehicleOnRoad(int x, int y) //definition
{
Return x+y;
}
Q5.Write a program to add two numbers using functions?
ans.
// sum of two numbers
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int sum(int,int); //declaration or prototype
void main()
{
int a=10;
int b = 20;
int s=0;
s=sum(a,b); //calling
cout<<"\n sum of two numbers : "<<s;
getch();
return;
}
// function definition
int sum( int a, int b )
{
int s1=0;
s1=a+b;
return s1;
or
return a+b;
}
Passing an Array to a Function
When an array is passed to a function the base address of the array is passed to the called function as an argument and it works as “call by reference.”
Q.Wap to return grade of a student on passing an array of marks?
Ans.
Prototype :
Char GetGrade( int [] ); // prototype
// my program for passing an array to function
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
char GetGrade( int [] ); // prototype
void main ()
{
char grade;
int mark[]={60,80,65,90,50};
grade = GetGrade( mark) ; //calling
cout <<”\n Grade of the student is :”<<grade;
getch();
return;
}
Chargetgrade( int x[5] ) //function definition
{
int s=0;
char grade[100];
for ( int i =0 ;i<5;i++)
s=s+x[i];
int marks = s/500; //average
if ( marks>=33 && marks<45 )
grade ='D';
else
if ( marks>=45 && marks<60 )
grade ='C';
else
if ( marks>=60 && marks<75 )
grade ='B';
else
if ( marks>=75 )
grade ='A';am
else
grade ='F';
return grade;
}
Q16.waf to find square of a number?
//
#
#
int sqr( int ); // prototype
void main()
{
int a =4;
int s=0
s=sqr( a); //calling
cout<<"\n square of number is :"<<s;
getch();
return;
}
//definition
int sqr( int x )
{
return x*x;
}
Q17.wap to find area of rectangular field?
ans.
prototype
float area( float, float)
calling
l=100;
b = 20;
float ar = area( l,b);
definition
float area ( float x, float y)
{
float arr;
arr= x * y;
return arr;
}
radius =5 cm
l v = 3.14 * r *r *r;
Q4.How much milk can be filled in bowl of radius 5 cm using a function.
Q5.WAf that return grade of student on marks received by him. Marks be passed as an array.
Q5a.write a program to convert lower case to upper case
Ans.
//convert lowercase to uppercase
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
Void main()
{
char name[10] =’abhinav’;
cout<<”\n upper case of the given character is:”<<strupr(name);
getch();
return;
}
}
Q18. waf to find how much gas can be accommodated in cylinder of
heightof 30 cm and radius of 10 cm. using function.
Ans.
// find gas capacity
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int vol( int,int ); //prototype
void main()
{
int r, h,v=0;
cout<<"Enter height of cylinder :";
cin>>h;
cout<<"\n Enter radius of cylinder :";
cin>>r;
v = vol( r,h); //calling
cout<<"Capacity or volume of gas is :"<<v;
getch();
return;
}
//definition
int vol ( int x, int y )
{
return 3.14 *x*x*y;
}
Q.19.Wap to find area of a rectangular field using functions?
Ans
//program for finding area
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Float Area ( int, int ); // prototype
Void main()
{
Int a, b;
float ar = 0;
a = 50;
b = 30;
ar= area( a, b ); // calling
cout<<”\n Area of rectangular field is :”<<arr;
getch();
return;
}
// definition
Float area( int x , int y )
{
Return x*y;
}
String user defined function
Q8.Wap to find length of a string?
Ans.
//length of the string
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Int strlength( char [] );
Void main()
{
Int length;
Char s1[30] =”India”;
length = strlength( s1 );
Cout<<”\n Length of the string is :”<<length;
Getch();
Return;
}
Int strlength( char s[])
{
For( int I =0 ; s[i]!=’\0’;i++)
;
Return i+1;
}
Q20. Wap to print a string in reverse order?
//printing string in reverse order
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Char [] reverse( char [] );
Void main()
{
Char s[30] =”Manik”;
Char s1[30];
Strcpy(s1,Reverse(s));
Cout<<”\n Reverse of the string is :”<<s1;
Getch();
Return;
}
Char x[30] reverse( s[30] )
{
For( int I =0;s[i]!=’\0’;i++)
;
K=0;
For ( int j =i+1;j>=0;j-- )
{
x[k] = s[j]
K++; }
Return x;
}
Q21.How many ways a function can be called ?
Ans. A Function can be called by two ways :-
1.Call by Value Method
2.Call by Reference
Q22.What is the difference between “call by value” and “call by reference method “.
Ans.
1.Call by Value
When a function is called “call by value method “ the called function works on the copies of the passed arguments of the calling function,so the values changed by the calling function will not reflect in the called arguments means no change in the original arguments value.
Ex.
//write function to say ‘y’ or ‘n’
char msg( char );//prototype
void main()
{
Char ch,reply;
Cout<<”\Pleas reply ..?”;
Cin>>reply;
Ch=msg( reply ); //calling
Cout<<”\n Are u attending class : “<<ch;
getch();
return;
}
char msg( char myreply )//definition
{
Cout<<”message function has been called…”;
return myreply;
}
1.Call by Reference
When a function is being called ‘call by reference’ method then the arguments of the called function actually works at the same location of the calling function arguments.
void swap( int & , int & ); // prototype –( & - address of )
void main()
{
int a=20, b = 50;
cout<<”\n before calling function “
cout<<”\n value of a is :”<<a;
cout<<”\n value of b is :”<<b;
cout<<”\n division of a and b is “<<a/b;
swap(a,b);
cout<<”\n After Calling function “
cout<<”\n value of a is :”<<a;
cout<<”\n value of b is :”<<b;
cout<<”\n division of a and b is “<<a/b ;
getch();
return;
}
void swap( int &x, int &y )
{
Int temp
temp = x;
x=y;
y =temp
}
Ex. 2
Char * Strrev( char [] )
Void main()
{
Char s[]=”Sparrow”
Cout<<”\n reverse of the string :”<<strrev(arr);
Getch()
Return;
}
Char * strrev( char x[] )
{
Char s1[10];
for( int I = 0 ;x[i]!= ‘\0’;i++)
s1[i] = x[5-i]; }
Q23.Write a function that displays season name ?
//display season
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
char * message(int ) ;
void main()
{
char seasonname[30];
int season;
cout<<"\n Enter which season it is ? :";
cin>>season;
strcpy(seasonname,message(season));
cout<<"\n you asked for this season :"<<seasonname;
getch();
return;
}
char * message( int season )
{
char newseason[30];
if ( season == 1 )
strcpy(newseason,"Summer");
else if (season == 2)
strcpy(newseason,"rainy");
else if (season == 3)
strcpy(newseason,"Autumn");
else
strcpy(newseason,"winter");
return newseason;
}
Class & Object
Q1.What is OOPs ?
Ans.
OOPs stands for Object Oriented Programming Language. In which each thing is viewed in the form of an Object.
Q2.What is an Object?.
Ans.
An object is a thing that has some Characterstic ,
State, behavior.
Ex. Mobile, chair , fan , watches etc.
Q3 What is a class?
A class is container for various kind of data members and functions?
Q4.What are Oops Properties?
Ans.
![]()
The following are the OOPS Properties :-
1. Data Abstraction
2. Data Encapsulation
3. Modularity
4. Inheritance
5. Polymorphism
Q5. Define oops properties ?
Ans.
1.Data Abstraction.
It is a property of oops in which only abstracted information is displayed by hiding the essential data.
Example : marksheet .
2.Encapsulation
This property bounds data with functions and works in an encapsulated form. Ex. Astronaut inside a rocket launcher
3.Modularity
This property bounds big project to be programmed and executed in a module form so that handling could be easier and faster.ex. Making a cup of tea
4.Inheritance
It is a property of oops in which a subclass inherits all the property of base class and with it, it can access & use data and functions of that ( super ) class.
5.Polymorphism
It is a capability of an object that can behave differently in different environment. Actually it is polymorph or multiform of the object capability.
Ex. Cat ( day ) - Domestic
Cat ( night) – Hunter
Q6.How to declare a Class?
Ans.

Syntax:
Class <class_name>
{
Private :
< Datatype > member name;
< Datatype > member name;
< Datatype > member name;
Protected :
Public :
<Return type > func. Name ( arguments…..)
{
//function method
}
} [object variable ];
Object Creation of a class :
Object of class can be created by two ways :
1.with the class definition itself
//created as above.
2.as a separate statement.
Syntax :
class_nam < object variable >;
Ex. Student ob;
Q7.What are the Access Specifiers?
Ans.
1.Private
These data members are neither inheritable nor accessible directly by object . The only way to access them is , by using public members functions.
2.Protected
Protected data members can be inherited by subclasses but are not directly accessible by object. But can be accessed by member function.
3.Public
These can be inherited by subclasses and can also be directly accessed by the object.
Ex.
Class student
{
Private :
Protected:
Public :
}
Q8.Wap to create a class student and get information about the student and display them?
Ans.
// class and objects
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{
private :
int rollno;
char name[30];
int marks;
public :
void getData()
{
cout<<"\n Enter your rollno :");
cin>>rollno;
cout<<"\n Enter your Name :");
cin>>name;
cout<<"\n Enter your Marks :");
cin>>marks;
}
void dispData()
{
cout<<"\n Rollno : "<<rollno;
cout<<"\n name :"<<name;
cout<<"\nmarks :"<<marks;
}
};
void main()
{
clrscr();
student ob; //object creation
ob.getData(); // . membership operator
ob.dispData();
getch();
return;
}
QA. Wap to access data members outside the class?
Function Definition outside the class
Class student
{
Private :
Int rollno;
Char name[30];
Float fee;
Int marks;
Char grade;
Public :
Void getdata(); //declaration
Void dispdata(); // declaration
};
public void student::getdata()
{
cout<<"\n Enter your rollno :");
cin>>rollno;
cout<<"\n Enter your Name :");
cin>>name;
cout<<"\n Enter your Fee :");
cin>>fee;
cout<<"\n Enter your marks :");
cin>>marks;
}
Public void student::dispData()
{
cout<<"\n Rollno : "<<rollno;
cout<"\n name :"<<name;
cout<<"\n Fee :"<<fee;
cout<<"\nmarks :"<<marks;
}
void main()
{
student ob;
ob.getdata();
ob.dispdata();
getch();
return;
}
Q8a. What is a resolution Operator (::)?
Ans.
A resolution operator is used to access class data members i.e.data variable & classe function outside of the class.
Classname :: variable_name
As in case of static
Student :: a //a is a static variable
Student :: member_fuction()
Q8A.Wap to create a class student and get his grade for marks achieved ?
// class and objects
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
// class and objects
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{
private :
int rollno;
char name[30];
float fee;
char grade;
int smarks[5];
int marks;
public :
void getData()
{
cout<<"\n Enter your rollno :");
cin>>rollno;
cout<<"\n Enter your Name :");
cin>>name;
cout<<"\n Enter your Fee :");
cin>>fee;
}
Int [] GetSubjectmark()
{
cout<<"\n Enter your marks :");
for ( int i = 0 ; i<5; i++)
cin>>smarks[i];
return
}
void dispData()
{
cout<<"\n Rollno : "<<rollno;
cout<<"\n name :"<<name;
cout<<"\n Fee :"<<fee;
cout<<"\nmarks :"<<marks;
cout<<”\n Grade : “<<grade;
}
Int GetMarks( smarks )
{
For( int j = 0;j<5;j++)
marks=marks+ smarks[j];
Return marks;
}
Char GetGrade( int marks )
{
if( marks>=33 && marks<45)
Grade=’D’;
else
If( marks>=45 && marks<60)
Grade=’C’;
Else
If( marks>=60 && marks<75)
Grade=’B’;
Else
If( marks>=75)
Grade=’A’;
Else
Grade=’F’;
return grade;
}
};
void main()
{
clrscr();
student ob; //object creation
ob.getData(); // . membership operator
ob.dispData();
ob.GetMarks(……)
ob.GetGrade();
ob.dispData();
getch();
return;
}
Note : class members are accessed by using membership operator ( . ).
Q9.What is nested class ?
Ans.
A class inside another class is known as nested class.
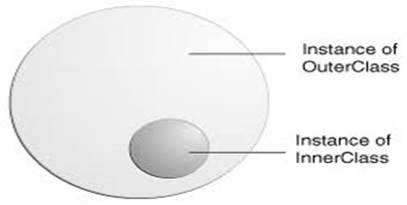
Example :-
// Nestclass example
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class A //outer class
{
private :
int a
public :
class B //nested class
{
private :
int b;
public :
void getIn()
{
cout<<"Enter value of b :";
cin>>b;
}
void dispIn()
{
cout<<"\n value of b is "<<b;
}
}ob1; //object creation of b nested class
void getOut()
{
cout<<"Enter value of a :";
cin>>a;
}
void dispOut()
{
cout<<"\n value of a is "<<a;
}
};
void main()
{
A ob; // object creation
ob.getOut();
ob.dispOut();
// B class
ob.ob1.getIn(); // nested class object
ob.ob1.dispIn();
getch();
return;
}
Q10A. Wap to make a class student with :
Fields/private: rollno, name,fee, marks,grade.
Public method:getdata(),dispdata(),char GetGrade( int )
Then display grade also.
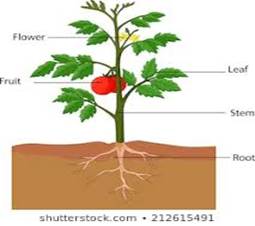
Q10A Wap to create a Tree class with
Class name : Tree
Data members : Root,Step, Branches, Leaf,buds
Member method : GetData()
DispData()
Nested : net of the bird
Class Name : Nest
Data members : kid1,kid2
Member method :
GetData()
DispData()
TotalMember()
Food_ArrangeMent() 
Q10B.Wap to create a nested class address of a student class Data members can be taken as rollno,name,class , section ,fee,marks And getData(), DispData() as public member functions . in the address class GetAddress() function to get address of student.?
Q11. How many ways an Object can access class members?
Ans.
1.Object as a variable
2.object as an array
3.Object as an array_of_Datamembers
4.Object as a Pointer
5.Object as an Pointer Array
Ex.
1.class <object_var> // Student ob;
2.class <object_var>[size] //Student ob[size]
3.class <object_var>.data_member[size]
//ex. Student ob.rollno[size]
4.class <*object_var>
5.class <*object_var[size])
Example
1.Object as an Array of a Class
When an object is created as array of object of a class then to many class data members information can be entered.
Student ob[size];//use for loop to access
Student ob[40];
Student ob[5];
Q8.Wap to create a class of productwith the following details :
Class : Product
Data members :
ProdId,ProdName,prodQty,ProdRate,gst,ProdAmt
,Remark
Member function:
GetProduct()
DispProduct()
CalcAmt()
Then display information of the product.
Ans.
//
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class Product
{
private :
int productId;
char productname[30];
float rate;
int Qty;
float amount;
char Remarks[50];
public :
void getData()
{
cout<<"\n Enter Product Id:");
cin>>productid;
cout<<"\n Enter Product Name :");
cin>>productname;
cout<<"\n Enter Rate :");
cin>>rate;
cout<<"\n Enter Quantity :");
cin>>quantity;
}
void dispData()
{
cout<<”\n PRODUCT INFORMATION”
cout<<”\n ===================”
cout<<"\n Product ID:"<<productid;
cout<"\n Product Name :"<<productname ;
cout<<"\n Rate :"<<rate;
cout<<"\n Quantity :"<<qty;
cout<<”\n Amount :”<<amount;
}
void calcAmt()
{
Amount = qty*rate;
}
};
void main()
{
clrscr();
product ob; //object creation
ob.getData();
ob.calcAmt();
ob.dispData();
}
getch();
return;
}
Q wap for using the above data for entering information of five (5) product.
Ans. Hint
void main()
{
clrscr();
product ob[5]; //object creation as an array
for(int i =0;i<5;i++)
{
ob[i].getData();
ob[i].calcAmt();
ob[i].dispData();
}
getch();
return;
}
Q.Wap to make a class name as product you have to enter information of product find total amount to be paid to the shopkeeper on ordering 5 product .
1.Object variable as a Pointer of a Class
When an object is created as array of object of a class then to many class data members information can be addressed.
Syntax :
Student *ob // object variable as pointer
Data member should be accessed by using membership operator or arrow operator (->)
Ob->data_member;
ob->getData();
Q8.Wap to create a class of product and get its detail also print them using object as pointer?
Ans.
//
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class Product
{
private :
int productId;
char productname[30];
float rate;
int Qty;
float amount;
char Remarks[50];
public :
void getData()
{
cout<<"\n Enter Product Id :");
cin>>productid;
cout<<"\n Enter Product Name :");
cin>>productname;
cout<<"\n Enter Rate :");
cin>>rate;
cout<<"\n Enter Quantity :");
cin>>quantity;
}
void dispData()
{
cout<<”\n PRODUCT INFORMATION”
cout<<”\n ===================”
cout<<"\n Product ID : "<<productid;
cout<"\n Product Name :"<<productname ;
cout<<"\n Rate : "<<rate;
cout<<"\n Quantity : "<<qty;
cout<<”\n Amount : ”<<amount;
}
void calcAmt()
{
Amount = qty*rate;
}
};
void main()
{
clrscr();
product *ob;//object creation as a pointer
ob->getData();
ob->calcAmt();
ob->dispData();
getch();
return;
}
Q10.List all the functions that can be defined in a class ?
Ans.
1.Member functions
2.Inline Functions
3.Static functions
4.Friend Functions
5.Virtual Functions
1.Member Function
A member function is function which is declared/defined inside a class without any specific keyword but using an access specifier to define its accessebility.
Public :
Void sum( int ,int); //declared
void sum( int a, int b)// definition
{
Cout<<” this is my member function”;
}
2.Inline Function
It used where the program code is very small. It is loaded as many times it is called from the main program. Memory overhead is a problem if code is bigger because multiple copies of the code are loaded on calling this result into memory expense. This is defined with inline keyword.
Ex.
Inline Int sum(int a, int b )
{
Return a+b;
}
3.Static function
A Static function is , which is defined with static keyword. This function is always loaded in the memory with class and it does not have any loading and allocation with the object. It is used to access static data variables These are accessed using class names .
Class student
{
Private :
static void myfun();
static int a;
Public Static void myfun( )
{
a= 10; // a is static.
}
Class name :: myfun()
Student :: myfun();
Student :: a;
4.Friend Function
Friend functions are the function that are declared inside the class with friend keyword but defined out class as a normal function and also these are access ed like a normal function. This function has all the privileges like member function and can access other data member like member function.
Friend void myfunc(); ///only declaration inside the class
Definition Outside the class
friend void myfunc()
{
///statement….
}
Calling:
Myfunc();
5.Virtual Function
A function which Is defined with virtual keyword is known as virtual function. This function is used to difine a class as abtract class that is used to implement overriding.
virtual void myfunc()
{
// body
}
Q10.Wap to illustrate use of all the functions.
Ans.
//my Program for Functions
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class MyFunc
{
public :
void init();
int inita();
int initb();
inline void mInline();
void mMember();
static void mStatic();
friend void mFriend();
virtual void mVirtual()=0;
};
class fnClass //: public Myfunc
{
private:
int a,b;
static int c;
public :
void init()
{
a=10;
b=20;
}
int inita()
{
return a;
}
int initb()
{
return b;
}
void mInline()
{
cout<<"\nInline function has been called.multiply."<<a+b;
return;
}
void mMember()
{
cout<<"\nMember function has been called.."<<a+b;
return;
}
static void mStatic()
{
cout<<"\nStatic function works with static variables .."<<c;
return;
}
virtual void mVirtual()
{
cout<<"\nVirtual fn has been called...";
return ;
}
friend void mFriend(fnClass);
};
fnClass ob;
int fnClass::c=30; //static variable using class name
void main()
{
clrscr();
ob.init();
ob.mInline();
ob.mMember();
fnClass::mStatic(); // resolution operator
ob.mVirtual();
mFriend(); // being called like a normal fun.
getch();
return;
}
void mFriend()
{
int x,y;
x=ob.inita();
y=ob.initb();
cout<<"\nfriend function has been called"<<x+y;
return;
}
Constructor & Distructor
Q1.What are Constructors ?
Ans.A Constructor are functions that have same name as of their class name.
Q2.Why constructors are required ?
Ans.
Constructors are required to initialize class data variables automatically with the object creation. We need not to call separately functions to initialize data members . Constructors are also used to implement overloading . when the program gets over destructor used to release the allocated memory to variables.that it does automatically.
stud() - playing
stud(school) - started taking school classes
stud(school,tuition) – tuition classes also
stud(school,tuition,homework) – home work
Q3.How many type of constructor are there ?
Ans. Constructors are of three (3) types i.e. :-
1.Default Constructor
This constructor is automatically called with the object creation . it does not have any parameter.
2.Parameterized Constructor
This has some parameters and is called with specific parameter number as it is identified by the no of arguments only.
3.Copy Constructor
This Constructor is called when one object is copied to another object.
4. Destructor
It is called when the object gets deleted or is not in existence or when the program gets over. The aim of the destructor is to release the allocated memory that was allocated with the object creation. It is written ~student().
Q4.How to implement Constructors ?
Ans.
Ex.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{
Private :
int rollno;
char name[30];
float fee;
public:
student() //default constructor
{
rollno =2343;
strcpy(name,"walleta");
fee = 900;
cout<<”\n default constructor has been called ”;
}
student( int mroll) //Parametarized.
{
rollno =mroll;
cout<<”\n parameterized constructor has been called with 1 parameter”
}
student(int mroll, char mname[30]) //Parametarized.
{
rollno =mroll;
stcpy(name,mname);
cout<<”\n parameterized constructor has been called with 2 parameter”
}
student(int mroll, char mname[30],float mfee) //Parametarized.
{
rollno =mroll;
stcpy(name,mname);
fee = mfee;
cout<<”\n parameterized constructor has been called with 3 parameter”
}
student ( student obnew ) // Copy constructor
{
Cout<<”\n Copy constructor has been called…”;
}
~student() // destructor
{
Cout<<”\n destructor has been called … “;
}
};
void main()
{
student ob;//default constructor
student (1006); //parameterized with 1
student (1006,"Robin"); //parameterized with 2
student(1006,"Robin",500); //parameterized with 3
student; ob1 = ob // copy constructor
getch();
return;
}
Q1.Write a program using constructors find area for different shapes Like square, rectangle , triangle .
Hint:
Constructor : area(),area(1),area(2),area(3)and display in msg.
Q2. Wap to find the volume of the following using constructors
1.Sphere r formula v = (4/3) * 3.14 * r*r*r;
2.Cylinder r,h v = 3.14 * r * r*h;
3.cuboid l,b,h v = l * b * h;
Print the volume in each case
Inheritance
Q1.What is inheritance ?
Ans.
Inheritance is a property of oops in which a subclass( child class ) inherits properties of base class (parent class ) or super class. To inherit a base class to a sub class we need to extend it.
Syntax
class A
{
}
class B : public A // inheriting A class
{
}
Q2.Why inheritance or what are the advantages of Inheritance ?
Ans.
1.Codes are reuseable.
2.Reduces development time
3. maintains systematic accessibility
Q3.What are the type of Inheritance in C++ ?
Ans..
1.Single Inheritance
2.Multi Level Inheritance
3.Multiple Inheritance
4.Hierarichal Inheritance
5.Hybrid Inheritance
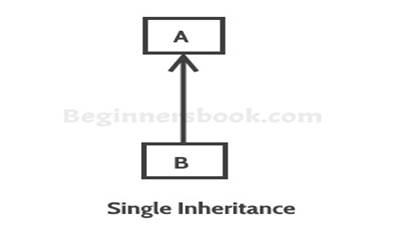
Single Inheritance
Single Inheritance: refers to a child and parent
class relationship where a class extends the another class.
Example 1.
Class A
{
Private :
int a;
protected :
int p1;
Public :
void displayA()
{
a=10;
cout<<“ This is my class A”;
}
};
Class B :public A // inheritance
{
Private :
int b;
public :
void displayB()
{
b=20;
p1=30;
cout<<“This class B “<<”p1=”<<p1<<”b=”<<b;
}
};
Void main()
{
Clrscr();
B ob;
Ob.displayA();
Ob.displayB();
getch();
return;
}
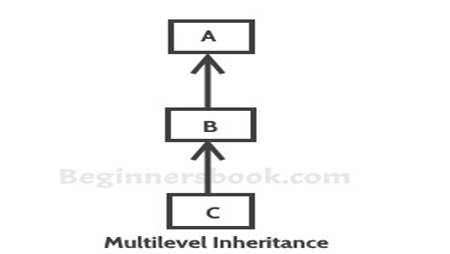
Multilevel inheritance:It refers
to a child and parent class relationship where a class extends the child class.
For example class C extends class B and class B extends class A.
Ex.
Class A
{
Protected :
int a;
protected :
int p1;
Public :
void displayA()
{
a=10;
cout<< “ This is my class A”;
}
};
Class B : public A
{
Private :
int b;
protected :
p2;
public :
void displayB()
{
b=20;
cout<< “This class B “<<”p1=”<<p1<<”b=”<<b;
}
};
Class C : public B
{
Private :
int c;
public :
Public void displayC()
{
c=30;
cout<< “This class C “<<”p1=”<<p1<<”p2=”<<p2<<”C=”<<c;
;
}
};
Void main()
{
clrscr();
C ob;
ob.displayA();
ob.displayB();
ob.displayC();
getch();
return;
}
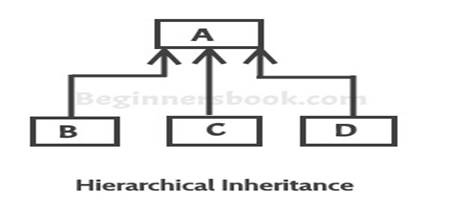
It refers to a child and parent class relationship where more than
one classes extends the same class. For example, classes B, C & D extends
the same class A.
Ex.
Class A
{
Private :
int a;
Public :
Public void displayA()
{
a=10;
cout<< “ This is my class A”;
}
};
Class B : public A
{
Private :
int b;
public :
Public void displayB()
{
b=20;
cout<< “This class B “<<”a=”<<a<<”b=”<<b;
}
};
Class C : public A
{
Private :
int c;
public :
Public void displayC()
{
c=30;
cout<< “This class C “<<”a=”<<a<<C=”<<c;
}
};
Class D : public A
{
Private :
int d;
public :
Public void displayD()
{
d=30;
cout<< “This class D “<<”a=”<<a<<”d=”<<d;
}
};
Void main()
{
clrscr();
B ob1;
C ob2;
D ob3;
ob1.displayB();
ob2.displayC();
ob3.displayD();
//
Ob1.displayA();
Ob2.displayA();
Ob3.displayA();
getch();
return;
}
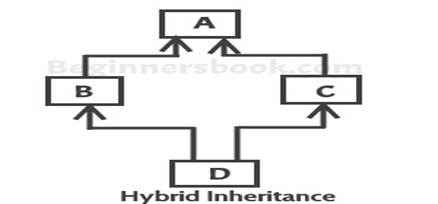
Multiple Inheritance:It refers to the concept of one
class extending more than one classes, which means a child class has two parent
classes. For example class C extends both classes A and B. .
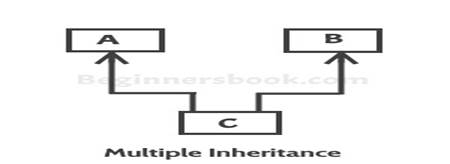
![]()
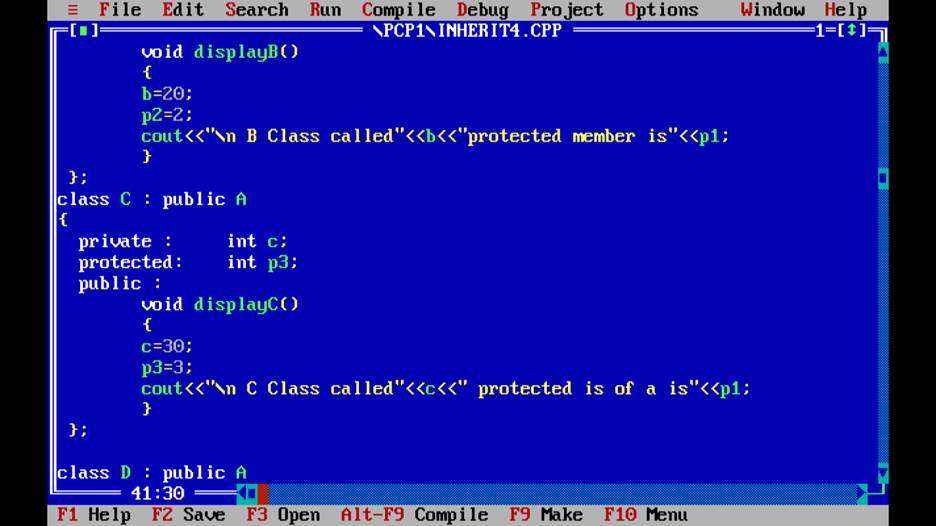
Combination of more than one types of inheritance in a single program. For example class A & B extends class C and another class D extends class A then this is a hybrid inheritance example because it is a combination of single and hierarchical inheritance. Not supported in c++
Polymorphism
Q1. What is polymorphism?
Ans. Polymorphism, represents capability of an object .that can behave differently in different environment means have the capabilityof performing in multiforms.
Q2. How polymorphism is implemented in c++?
Ans. polymorphism is implemented in c++ by two ways:-
1.by Overloading
2.by Overriding
Q3.What is Binding ?
Ans.
Binding is a process in which all variables and member functionsare converted into their memory locations means once binding is done then no names of variables and classes or functions will be used rather their addresses and the defined link of calling will be used in the memory while running a program.
Q4.How many types of Binding are there?
Ans. Bindings are of two types :-
1.Static Binding
2.Dynamic Binding
Q5.What is static Binding ?
Ans Static Bindingis done at the compile time.
Ex.of staticBinding is implemented by overloading using either by constructors orby functions overloading
Q6.What is overloading ?
Ans.Overloading means a function or a constructor is being identifiedby its signature (different arguments )
Sum(a,b)
Sum(a,b,c)
Sum(a,b,c,d)
//Exampl of Overloading by constructor
#include<iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include<string.h>
class student
{
private :
int rollno;
char name[30];
float fee;
public:
student() //default constructor
{
rollno =2343;
strcpy(name,"Streak");
fee = 900;
}
student( int mroll) //Parametarized.
{
rollno =mroll;
}
student(int mroll, char mname[30])
//Parametarized
{
rollno =mroll;
strcpy(name,mname);
}
display()
{
cout<<”\n Rollno :”<<rollno;
cout<<”\n name :”<<name;
cout<<”\n fee :”<<fee;
}
};
void main()
{
clrscr();
student ob; //default
ob.display();
student ob1(1006); //parameterized constructr with 1 arg.
ob1.display();
student ob2(1006,"java");//parametirzed with 2..
ob2.display();
getch();
return;
}
//Exampl of Overloading by Method
#include<iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
class student
{
Private :
int rollno;
char name[30];
float fee;
public:
getdata() //no parameter
{
rollno =2343;
stcpy(name,"Streak");
fee = 900;
}
getdata( int mroll) //Parametarized.
{
rollno =mroll;
}
getdata(int mroll, char mname[30])//Parametarized
{
rollno =mroll;
stcpy(name,mname;
}
};
void main()
{
student ob;
ob.getdata();
ob.getdata(1006);
ob.getdata(1006,"java");
getch();
return;
}
Q. What is C++ Operators Overloading ?
Ans. Operator overloading is used to overload an operator or redefines most of the operators to perform the operation on the user-defined data type.
Ex. Adding variables .The advantage of Operators overloading is to perform different operations on the same operand.
Operator that cannot be overloaded are as follows:
o Scope operator (::)
o Sizeof
o member selector(.)
o member pointer selector(*)
o ternary operator(?:)
o
Syntax of Operator Overloading
return_type class_name : : operator op(arg_list)
{
// body of the function.
}
operator op is an operator function where op is the operator being overloaded, and the operator is the keyword.
Rules for Operator Overloading
o Existing operators can only be overloaded, but the new operators cannot be overloaded.
o The overloaded operator contains atleast one operand of the user-defined data type.
o We cannot use friend function to overload certain operators. However, the member function can be used to overload those operators.
o When unary operators are overloaded through a member function take no explicit arguments, but, if they are overloaded by a friend function, takes one argument.
Ex.
void operator ++ () operator function is defined (inside A class).
// program to overload the unary operator ++.
#include <iostream.h>
//using namespace std;
class A
{
private:
int x,y,z; //x is variable
public:
A()
{
x=1;
y=2;
z=3;
}
// x is function here
void operator ++()
{
x = x+4;
y = y+5;
z = z+6;
}
void print()
{
cout<<"The value of x Count is: "<<x;
cout<<"The value of y Count is: "<<y;
cout<<"The value of z Count is: "<<z;
}
};
int main()
{
clrscr();
A ob;
++ob;//calling of a function "void operator ++()"
ob.print();
getch();
return 0;
}
Output:
The Count is: ..
Binary operator overloading.
// program to overload the binary operators.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
Private :
int x;
public:
A()
{
x=5;
}
A(int i)
{
x=i;
}
void operator+(A);
void display();
};
void A :: operator+(A a)
{
int m = x+a.x;
cout<<"Addition of objects is : "<<m;
}
int main()
{
A ob1(5);
A ob2(4);
Cout<<”\n Addition of object is :”<<ob1+ob2;
return 0;
}
Output:
The result of the addition of two objects is : 9
Q7.What is late binding?
Ans.Binding that takes place at runtime is known as late binding or dynamic binding. In late binding again the link, the memory location that were bound at compile time will again be linked with each other as defined in the program to run it smoothly.
The late binding process is achieved by overriding.
Q9.What is Overriding ?
Ans. Overriding, when a function is defined with the same name in the subclass as it’s base class function name.
Example
//my overriding program ( as overwritten)
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class A
{
private :
int a;
public :
void display()
{
a=10;
cout<<"\n A Class is called and value of a is :"<<a;
}
};
class B : public A
{
private :
int b;
public :
void display()
{
b=20;
cout<<"\n B Class is called and value of b is :"<<b;
}
};
void main()
{
B ob;
ob.display();
getch();
return;
}
Q10.What is an Abstract class?
Ans.
An abstract class is a class which is for the purpose of getting implemented by the other classes or sub classes.Abstract class cannot be instantiated means no object can be created of this class.so, abstract is use for implementation purpose only.
Q9.What is a virtual function?
Ans . A virtual function is a function which is used to implement latebinding or runtime polymorphism. It is declared/defined with virtual keyword.
syntax
virtual void display()
{
}
Q10.What is Pure virtual function?
Ans.
A pure virtual function is declared in a class with
virtual void display() =0;
and if a class is defined with pure virtual function then it becomes an abstract class. Means its object cannot created. And is implemented by subclass.
Also if a subclass does not define the pure function then that also become an abstract class.
Q11.How to implement runtime polymorphism with virtual function?
ans.
//my overriding program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class A
{
private :
int a;
public :
void display()
{
Cout<<”\n This is pure virtual function class “;
}
};
class B : public A
{
private :
int b;
public :
void display()
{
b=20;
cout<<"\n B Class is called,value of b is :"<<b;
}
};
void main()
{
B ob;
Ob.display();
getch();
return;
}
Ex.2 - Implementing overriding using a pointer
virtual, the call to the function is resolved at runtime, compiler determines the type of the object at runtime and calls the appropriate function.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//Parent class or super class or base class
class A{
public:
virtual void display()
{
cout<<"This is A class Function";
}
};
class B : public A
{
public:
void display(){
cout<<" B class function";
}
};
int main(){
A*ob;
//Ob->display()
ob = new B();// new is an operator used to create and allocate memory at runtime only
ob->display();// at run time
return 0;
}
Result :
Q12. Write a program to inherit an animal class in a bird class and thendisplay animal class called and bird class called using virtual function.
Class A
{
Private : a;
Public :
Class B
{
Public : b;
}ob1;
Void display()
{
Cout<<”\n class a has been called”
}
} ob;
1.How to access B data member.
Cout<<ob.ob1.b;
2.how to define display() outside of the class?
A::display()
Pointer
Q1.What is a Pointer ?
Ans. A pointer is a variable that points to the address of another variable.
int num;
int *p; // pointer declaration
p= # //storing address of another variable
Q2. Why to use Pointers ?
Ans.
· To pass arguments by reference. ...
· For accessing array elements. ...
· To return multiple values. ...
· Dynamic memory allocation : We can use pointers to dynamically allocate memory using malloc calloc. ...
· To implement data structures. Ex. linklist...
· To do system level programming where memory addresses are useful.
Ex.Socket programming
Q3.How to Declare a Pointer ?
Ans.
<data_type> *var;
Ex.
int *p; // p is pointer of integer type
double *dp; // pointer to a double
float *fp; // pointer to a float
char *ch // pointer to character
Q4.How to initialize a Pointer?
Ans.
*p=NULL;
Q5.What is NULL ?.
Ans. NULL is a pointer and keyword as well. It is a pointer that does not point to anywhere. So this can be assigned as value to other pointer variable.
Ex.
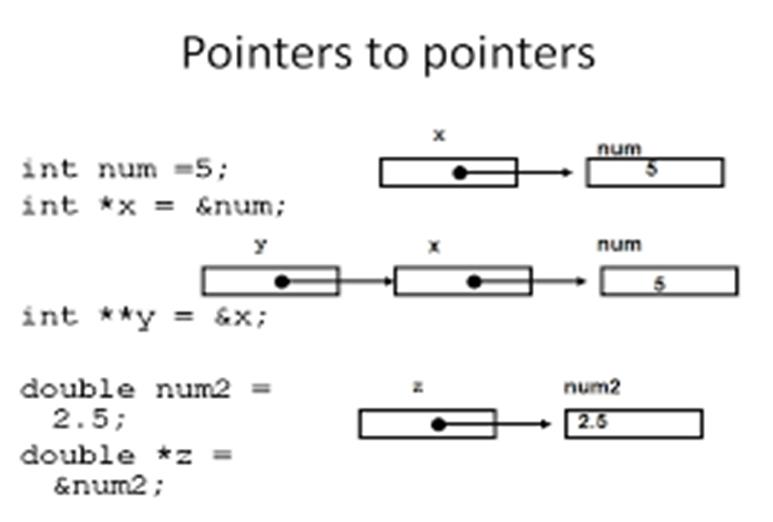
Q6. My first program on pointers?
Ans.
#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Pointer declaration
int *p, var=101;
//Assignment
p = &var;
cout<<"Value of variable : "<< var <<endl;
cout<<"Address of variable: "<<&var<<endl;
cout<<"Value of var using pointer : "<<*p;
cout<<"Address of var using pointer: "<<p<<endl;
cout<<"Address of p: "<<&p<<endl;
return 0;
}
![]() Note :
Note :
o p - > address of the variable
o *p - value of the variable
Output:
Address of var: 0x7fff5dfffc0c
Address of var pointer : 0x7fff5dfffc0c
Address of p: 0x7fff5dfffc10
Value of var: 101
Value of var pointer : 101
Ex.
a=10
b=20
*p1,*p2;
P1=&a;
P2=&b;
cout<<”\n variable “<<*p1+*p2;
Cout<<”value of a and b is :”<<*p1+*p2;
Q7.What are the types of pointer?
Ans.There are eight different types of pointers they are:
ü Null pointer.
ü Void pointer.
ü Wild pointer.
ü Dangling pointer.
ü Complex pointer. void
ü Near pointer.
ü Far pointer.
ü Huge pointer.
1.Null Pointer:
A pointer that points to nothing is called a Null pointer. Some advantages of Null pointer are:
· We can initialize a pointer variable when that pointer variable is not assigned any actual memory address.
· We can pass a null pointer to a function argument when we are not willing to pass any actual memory address.
Example 1:
int *a = NULL;
Example 2:
int fun(int *ptr)
{
return 15;
}
fun(NULL);
Example 3:
if (a != NULL)
{ //some code}
else
{//some code}
Void Pointer:
The void pointer within C/c++ is a pointer that is not allied with any data types. This points to some data location within the storage area means points to that address of variables. It is also known as a general-purpose pointer. In C, malloc() and calloc() functions return void * or generic pointers.
Example:
int x= 10;
char y= ‘a’;
void *p= &x //void pointer contains address of int x
p = &y //void pointer holds of char y
Wild Pointer:
Pointers that are not initialized are called wild pointers. This pointer may be initialized to a non-NULL garbage value which may not be a valid address.
Example:
int main()
{
int *p; // wild pointer
*p= 10;
}
Remember if a pointer p points to any known variable, then it is not a wild pointer. In the below program p is a wild pointer until it points to x.
int main()
{
int = *p; // wild pointer
int x= 20;
p= &x // p is not a wild pointer now
}
Dangling Pointer:
A pointer that points to a memory location that has been deleted is called a dangling pointer.
Example 1:
Deallocation of memory:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int *ptr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
}
Example 2:
Function call:
#include<stdio.h>
int *fun()
{
int y= 15;
return &y
}
int main()
{
int *p = func()
fflush(stdin)
printf(“%d”, *p);
return 0;
}
Complex Pointer:
Before knowing how to read complex pointers then you should first know associativity and precedence.
Associativity: Order operators of equal precedence within an expression are employed.
Precedence: Operator precedence describes the order in which C reads expressions.
|
Operator |
Precedence |
Associative |
|
(),[] |
1 |
Left to Right |
|
*,Identifier |
2 |
Right to Left |
|
Data Type |
3 |
– |
· (): this operator is used to declare and define the function.
· []: this is an array subscript operator.
· *: this is a pointer operator.
· Identifier: this is the name of a pointer.
· Data type: this is the type of variable.
Example:
int (*p)(int (*)[3], int (*)void))
Near Pointer:
· Near pointer means a pointer that is utilized to bit address of up to 16 bits within a given section of that computer memory which is 16 bit enabled.
· It can only access data of the small size of about 64 kb within a given period, which is the main disadvantage of this type of pointer.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a= 300;
int near* ptr;
ptr= &a;
printf(“%d”,sizeof ptr);
return 0;
}
Output: 3
Far Pointer:
· A far pointer is typically 32 bit which can access memory outside that current segment.
· To utilize the far pointer, the compiler allows a segment register to save segment address, then another register to save offset inside the current segment.
Example:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a= 10;
int far *ptr;
ptr=&a;
cout<<sizeof(ptr);
return 0;
}
Huge Pointer:
· Same as far pointer huge pointer is also typically 32 bit which can access outside the segment.
· A far pointer that is fixed and hence that part of that sector within which they are located cannot be changed in any way; huge pointers can be changed.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char huge *far *a;
printf(“%d%d%d”, sizeof(a), size(*a), sizeof(**a));
return 0;
}
Output: 4 4 1.
Struct pointer:
· Pointers can be utilized to refer to a struct by its address. This helps pass structs to a function.
· The pointer can be dereferenced by the * operator.
· The -> operator dereferences the pointer to the left operand and later accesses the value of a member of the right operand.
Advantages of pointers in C/c++:
· Pointers permit the management of structures that are allocated memory dynamically.
· Pointers make it possible to pass the address of structure rather than the entire structure to the functions.
Q8.What is Pointer and Arrays ?
Ans. An array name is itself a pointer to the base address means it contains address of the first element of the array
Int Arr[5];
Arr // is pointer to base address i.e. address of first element
Q9.How to assign array address to pointer?
Ans.
int *p;
int arr[]={10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
P=Arr; // no & operator is required
Q10. How to traverse an array using pointer?
Ans.
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
//using namespace std;
int main()
{
clrscr();
int *p;
int arr[]={10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
p = arr; //array address is assigned
![]() for(int
i=0; i<5;i++)
for(int
i=0; i<5;i++)
{
cout<<*p<<endl;
p++; // address is incremented of array
}
return 0;
}
Output : is array value
Q.Wap to traverse an array using pointer arithmetic?
Q10.How to find length of a string using pointer ?
Q11.Array as a pointer and increment, decrement oprn?
Ans.
Ex:
a=10
*p1,**p2,***p3;………**p198
P1=&a;
*p2=p1
**p3=*p2
Value = *p1
Address = p1
Value = **p2
Address = *p2
Value = ***p3
Address = **p3
….
Value = ****..p198
Address = ****..p198
Q12.How to use increment and decrement operator with pointer?
Q13.What is the difference between
Int *p=NULL
P=Arr // arr is an array
P=&Arr[0]
Q14.find output of the following program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int numbers[5];
int * p;
p = numbers;
*p = 10;
p++;
*p = 20;
p = &numbers[2];
*p = 30;
p = numbers + 3;
*p = 40;
p = numbers;
*(p+4) = 50;
for (int n=0; n<5; n++)
cout << numbers[n] << ", ";
return 0;
}
Output:
Q15.Writ a program to add two numbers using a pointer
Q16.Assume you are having five variable with values
Int a=10;
Int b=20;
Int c=30;
Int d=40;
Int e=50;
Int *p1,**p2,***p3,****p4,*****p5;
Now
Each pointer is having address that the previous pointer is pointer to , so you have find value of *****p5?
Q . How to change value of a variable by pointer?
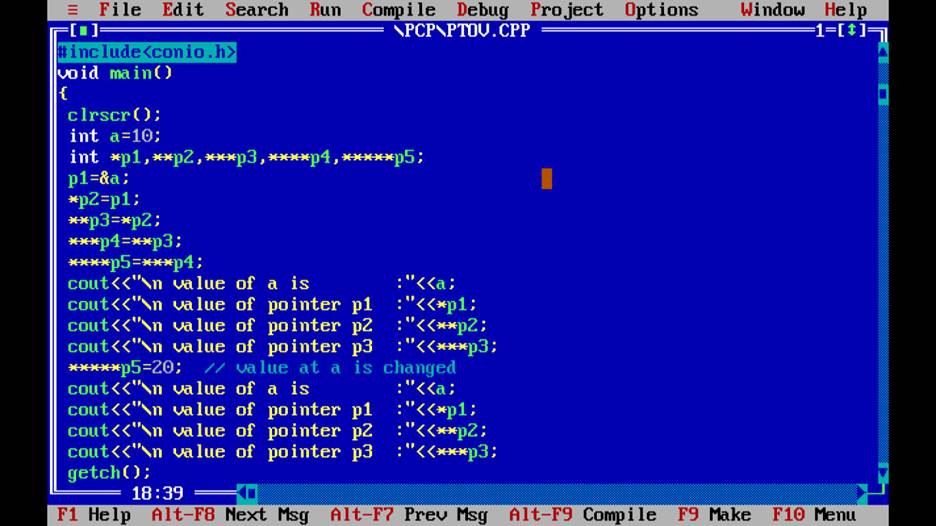
Passing Pointer to a Function
A pointer can be passed to a function by reference.
Ex.
//passing pointer to a function
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int sum( int *, int * );
void main()
{
Int a=10;
Int b =20;
Int s = 0;
Cout<<”\n before calling :”;
Cout<<”\n value of a is :”<<a;
Cout<<”\n value of b is :”<<b;
s = sum( &a, &b);
cout<<”\n after calling sum”;
Cout<<”\n value of a is :”<<a;
Cout<<”\n value of b is :”<<b;
cout<<”\n sum is :”<<s;
getch();
return;
}
Int sum( int *x, int *y )
{
int *temp;
*temp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=*temp;
return *x+*y;
}
Q.wap to swap the addresses of two servers using pointer ?
Ans.
CiscoServer = “192.101.90.206”
IBMServer=”172.107.80.105”
Void swap ( char *, char * );
Q15.What is Dynamic Memory?
Ans.
Dynamic memory is a system memory that is required at runtime by the programs for running the application in that environment.
Q16.Why Dynamic Memory ?
Ans.
As Memory allocation is a very important part of software development so when the program is loaded into the system memory, the memory region allocated to the program is divided into three broad regions: stack, heap and code. All these parts (various components) of the programuses dynamic memory at run time to execute the program.
Q17.How Dynamic Memory is Allocated ?
Ans.
The is allocated from the unallocated memory area that is from Heap.A heap is a free store memory area that is always allocated or used by the programs at runtime and then after use, this memory is released.Dynamic memory management in C/C++ programming language is performed via following
Two ways :
1.By using newOperator
2.By using memory allocation functions
A.By Using new Operators
1.new –This operatoris used to allocate memory Dynamically. new is a keyword also.
Ex.
int *p = new int() // nothing
int *p = new int(10) // initialized with 10
int p[] = new int p[10];
This memory is de-allocated by usingdelete operator i.e.
Delete p;
Q18.Wap to illustrate use of new and delete operator
Ans.
// using pointer
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int *p ;
p= new int(10);
cout<<”\n Value of the pointer is :”<<*p;
delete p;
getch();
return;
}
B.By Using Functions
There are four dynamic memory allocation functions of the C/c++ programming language are defined in the C standard library header file <stdlib.h>. These are :-
1.malloc()-used to allocate memory for single block
2.calloc()-used to allocate memory for multi block
3.realloc()-used to reallocated if any change in size.
4.free()-used to free up or release the allocated memory.
malloc() calloc() functions takes a single parameter, which is the size of the requested memory area in bytes. It returns a pointer to the allocated memory.
Q5.What is the Syntax of Dynamic Memory Allocation Functions?
Ans.
Ex.
ptr = (cast-type*) malloc(byte-size)
p = (int*) malloc(100);
p = ( char *) malloc(10);
p = (int * ) calloc (n, element_size);
p= (int * ) calloc( 10,sizeof( int ) );
p = (float*) calloc(5, sizeof(float));
This statement allocates contiguous space in memory for 5 elements each with the size of the float.
Q.Wap to Allocate memory using malloc() to a string with size 10 bytes and display its contents?
Ans.
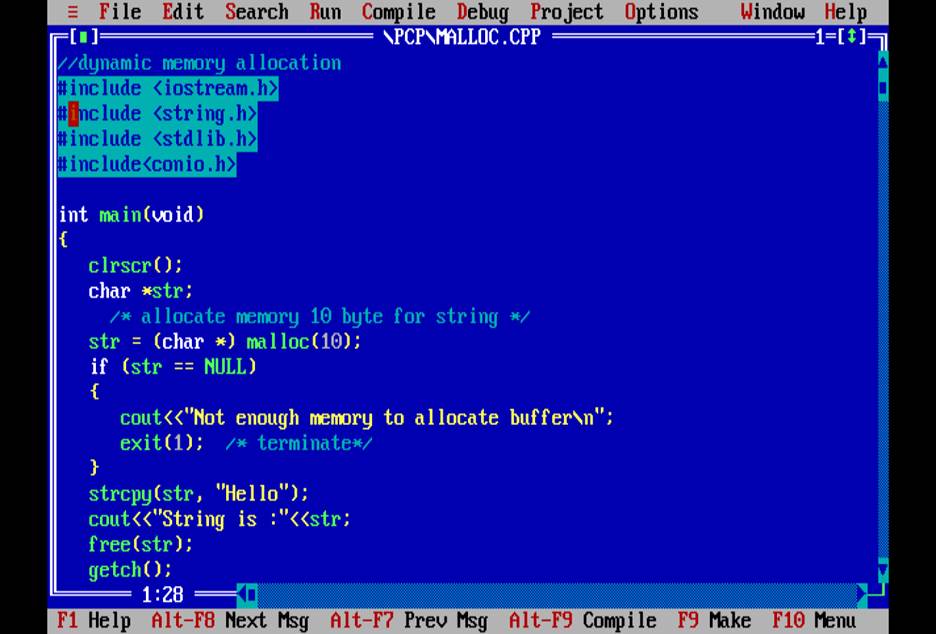
Q.Wap to Allocate memory using calloc() to a string of 10 elements and display its contents?
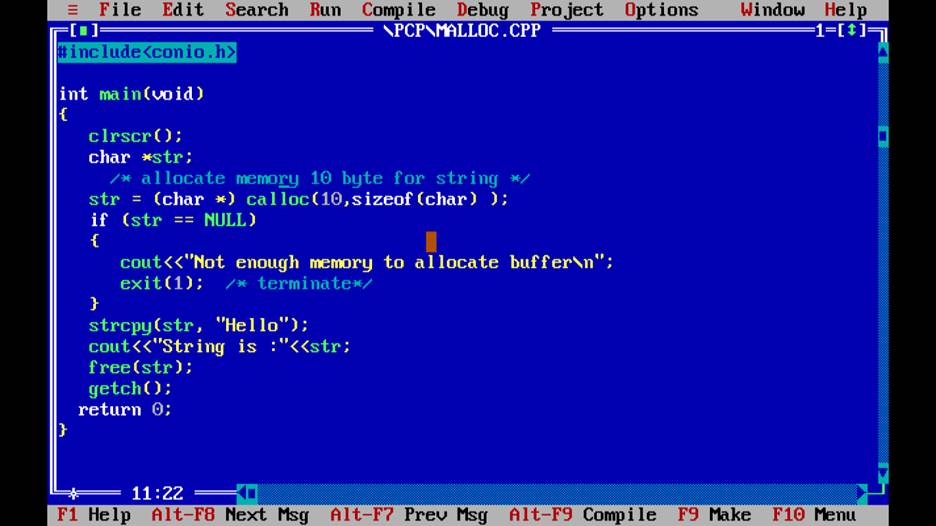
Q Reallocate memory for changed size of the string ?
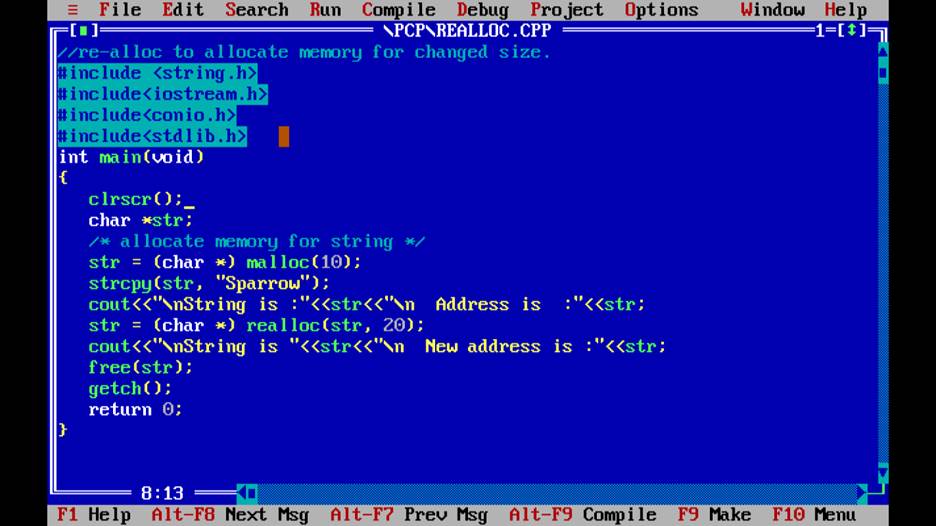
Q What is a Memory Leak?
Ans.
Memory leak when we allocate memory by using new keyword and forgets to deallocate the memory by using delete() function or delete[] operator. One of the most memory leakage occurs in C++ by using wrong delete operator which should be used to free a single allocated memory space, whereas the delete [] operator should be used to free an array of data values ex.erro like “insufficient memory error”
Pointer test
|
1. Which of the following is the proper declaration of a pointer? |
File Handling
Q1.What is file handling?
Ans.
File Handling are the operations that are performed ona file like reading , writing,updating and deleting etc.beside this taking backup of a file and Restoring data back to the system is also a task of file handling.
Q2. Why file handling ?
Ans.
As reading / writing to file is a task for saving information in a file for long time so becomes essential to do these task.
Q3.What is a file?
Ans.
A file is used to store information where data can be stored
and retrieved as and when required.
or
A file is set of records & records are set of entities that are rollno,name,class , section ,fee ,marks etc.
Q4.What is stream?
Ans.
A Stream is a flow of bytes that can be inflow or outflow.
In c++, the following are the stream classes :
iostream - input /output
istream - input
ostream - output
IOS is a top class of all the classes.
file stream
fstream - input /output
ifstream - input from a file.
ofstream - oupt into a file
Q4A What is stream Hierarchi?
Ans:
q5.What are bytes?
Ans bytes are smallest unit of measuring size of data space.
Q6.How many type of file orgnization are?
Ans File as per orgniation are of two types :-
1.Sequential File Access : In this file record is access
one by one in sequence.
2.Random file Access
In this type of file organization file is access on the basis of a key .Itmuch faster than sequential file access and record can be directly accessedon the basis of key given. it normally used for dat type or binary files
Q7. What are the types of file ?
Ans .
Files can be of two type
1.text file with .txt extension
2.Data file with .Dat extension
Q8.What is a .txt file ?
Ans.
A Text file is a simple file used to store information in text format
these file contains code for line feed and carriage return so when are opened the character stored in this are converted so as compared to dat it will be little slower for huge data.
Q9. What is at Dat File ?
These files are binary files and are read directly in the same form as theyare so are much faster then txt files similary at writing also these are saved as it is means no conversion takes place.
Q10.What all operations can be performed on a file ?
Ans
1.Openig of file
2.Check for data if you are reading somthing from it.
3.Write to File
4.Read/edit a file
5.Display Data
6.close a file
Q11.What are the mode of a file opening ?
Ans.
mode are used in a file operation for opening a file in read,write and append mode normally this will be used with fstream class object.
ios::in = opens a file in Read mode
ios::out - opens a file in write mode(overwritten )
ios::app - write data to file i.e. at the end of record
means if you have 10 records append mode will add 11th the record
ios:binary - in this mode file will be opened in binary form means in the0s and 1s no coversion and also not easily understandablefor such files you need to have the same program through which u have saved data .
Q12.What are the functions that are used to work with file?
ans. The following are the function used to perform various operation on a file :-
1.Open()
2.read()
3.write()
4.close()
5.eof()
6.bof()
Syntax of the File Function
fstream myFile;
myFile.open ("student.dat", ios::in | ios::out | ios::binary);
Q13. How to create a text file ?
ex1.
// text file creation using direct input
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
void main()
{
char str[150]="I am learning c++ “;
cout<<str;
ofstream fout;
fout.open("myfile.txt"); //opening a file for writing fout<<str; // writing to file
fout.close();
cout<<"file written successfully";
getch();
return;
}
Q14.How to save a message to a text file using ?
Ans.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
void main()
{
char msg[100];
cout<<"\n Enter your text msg.:";
cin>>msg;
cout<<msg;
ofstream fout;
fout.open("myfile.txt");
fout<<msg;
fout.close();
cout<<"file written successfully";
getch();
return;
}
Q15.How to Create a file with name of your choice and save data to it.?
ans.
// creating a .txt file
#include<iostream.>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
void main()
{
fstream fp;
char fname[10];
char msg[100];
cout<<"\enter your file name :";
cin>>fname;
fp.open(fname,ios::out ); // writting mode
if (!fp) or (fp==null )
cout<<"file opening error");
exit(0);
else
cout<<"Enter your text :";
cin>>msg;
fp<<" i like eating apple which are very healthy fruit one should take";
fp<<" atleast one apple a day "'
fp<<msg;
fp.close();
cout<<"file written successfully";
getch();
return;
}
//dir *.txt
Q16.How to read a text file ?
Ans.
#include<iostream.>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
void main()
{
fstream fp;
char fname[10];
char msg[100];
cout<<"\enter your file name to open :";
cin>>fname;
fp.open(fname,ios::in ); // reading
if (!fp) or (fp==null )
cout<<"file could not be opened");
else
fp>>msg;
cout<<msg;
fp.close();
cout<<"file reading is successfully";
getch();
return;
}
Q. Wap to list code of your .cpp File ?
Q wap to find no of characters in a file ?
Ans.
#include<fstream>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("out.txt");
int count = 0;
char ch;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.get(ch);
count++;
}
cout << "Number of characters in file are " << count;
fin.close();
return 0;
}
//find number of words in a file
#include<fstream>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("out.txt");
int count = 0;
char word[30];
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin >> word;
count++;
}
cout << "Number of words in file are " << count;
fin.close();
return 0;
}
Q.Program to count number of lines in a file ?
Ans.
#include<fstream>
#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("out.txt");
if ( !fin )
cout<<”\n file open error “;
int count = 0;
char str[80];
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.getline(str,80);
cout<<str;
count++;
}
cout << "Number of lines in file are " << count;
fin.close();
return 0;
}
Q.Program to copy contents of a file to another file.?
Ans.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
Or
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("myfirst.cpp");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("mysecond.cpp");
char ch;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.get(ch);
fout << ch;
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
return 0;
}
Q17. WAP to save 5 student’s information to a file student file ?
Ans.
// my program for writing data to file
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
void main()
{
int age;
char name[30];
int ans;
fstream fp;
fp.open(“myfile.txt”,IOS::OUT);
while (1)
{
cout<<"\n Enter your name :";
cin>>name;
cout<<"\nEnter your age :";
cin>>age;
fp<<name<<age; //writing to a file
cout<<"\n Any more entry : 1-yes 0 - no";
cin>>ans;
if (ans==0 )
break;
}
fp.close();
cout<<"file writing is over ";
getch();
}
Q 5.Wap to copy Homewrk.txt Classwrk.txt and then display
classwrk.txt 's contents?
Q 6.Wap to search your first name in the file ?
Q 7.wap to that can be used to view your c program file istead of any notepad or turbo compiler?
Data Files
Q16.wap to computerize a banking system which having
information
Had Office : Account details
Acc_no
Acc_Name
Address; //nested class
Bank_name;
Rate;
Payment
withdraw
Balance
time_period;
Account_Type
branch office : Branch _Account // inhert main bank structure
Acc_no
Acc_Name
Address; //nested class
Bank_name;
Rate;
Payment
withdraw
Balance
time_period;
Account_Type
Functions
Account_get_Data();
Account_Disp_Data();
Deposit();
Withdraw();
Balance()
Interest_Calculation()
Reporting
1.Account Holder Reporting
2.Deposit Reports
3.Withdrawal Sheet
4.Balance status Reporting
Q15.Wap to enter account holders details in a file and Display them?
Ans.
// My Banking System
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<fstream.h>
class Account
{
private :
int Accno;
char name[30];
char AccType;
How to Start a Project
/*/
user authentication window
User Name : ..........
Password : ..........
login y/n
*/
//my user authencation program
<iostream.h>
<conio.h>
class user{
private :
char UserId[30];
char Password[10];
public :
void GetUserInfo()
{
cout<<"\n User Name :";
cin>>userId;
cout<<"\n Password :";
cin>>Password;
}
void DispUserInfo()
{
cout<<"\n User Name :"<<userId;
cout"\n\n";
cout<<"\n Password :"<<password;
}
};
// draw your Menu
My Bank_name
=============
1.Open your Account
2.Activate your Account
3.Deposit
4.Withdrawal
6
file saving
//file saving
#include<iostream.h>
..
.
void main()
{
fstream fp;
fp.open("mybank.dat",ios::out | ios::app )
}
Q18.What are the functions used to work with binary file ?
Methods should be used as :
#include<fstream.h>
fstream fp;
1.file opening
fp.open("mybank.dat",ios::in | ios::binary ) // binary read
fp.open("mybank.dat",ios::out | ios::binary ) // binary write
fp.open("mybank.dat",ios::out | ios::app | ios::binary ) // binary write
2.check whether file opened
if (!fp)
cout<<"file could not be opened or opeing error";
else
3. if (!fp.eof()) // checking eof() end of file
4. fp.read( (char *) &ob, sizeof(ob))
5. fp.write( (char *) &ob, sizeof(ob))
reading
6. posi = fp.tellg();
7. get file pointer
fp.seekg(posi);
fp.seekg(0,ios::beg);
fp.seekg(0,ios::cur);
fp.seekg(0,ios::end);
writing
8. posi = fp.tellp();
9. put file pointer
fp.seekp(posi);
fp.seekp(0,ios::beg);
fp.seekp(0,ios::cur);
fp.seekp(0,ios::end);
10.fp.close()
Q.Wap to add, modify , delete and display data in a binary file ?
Ans.
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
Private :
int rollno;
char name[50];
public:
void getData()
{
cout << "\nEnter Roll no. ";
cin >>rollno;
cout << "Enter name of student ";
cin.getline(name,50);
}
void showData()
{
cout << "\nRoll no. : " <<rollno;
cout << "\nStudent Name : " << name;
}
int retRollno()
{
return rollno;
}
};
/*
* function to write in a binary file.
*/
void write_record()
{
ofstream outFile;
outFile.open("student.dat", ios::binary | ios::app);
Student ob;
ob.getData();
outFile.write((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob));
outFile.close();
}
/*
* function to display records of file
*/
void display()
{
ifstream inFile;
inFile.open("student.dat", ios::binary);
Student ob;
while(inFile.read((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob)))
{
ob.showData();
}
inFile.close();
}
/*
* function to search and display from binary file
*/
void search(int nRollno)
{
ifstream inFile;
inFile.open("student.dat", ios::binary);
Student ob;
while(inFile.read((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob)))
{
if(ob.retRollno() == nRollno)
{
ob.showData();
}
}
inFile.close();
}
/*
* function to delete a record
*/
void delete_record(int nRollno)
{
Student ob;
ifstream inFile;
inFile.open("student.dat", ios::binary);
ofstream outFile;
outFile.open("temp.dat", ios::out | ios::binary);
while(inFile.read((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob)))
{
if(obj.retRollno() != nRollno)
{
outFile.write((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob));
}
}
inFile.close();
outFile.close();
remove("student.dat");
rename("temp.dat", "student.dat");
}
/*
* function to modify a record
*/
void modify_record(int n)
{
fstream file;
file.open("student.dat",ios::in | ios::out);
Student ob;
while(file.read((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob)))
{
if(ob.retRollno() == nRollno)
{
cout << "\nEnter the new details of student";
ob.getData();
int pos = -1 * sizeof(ob);
file.seekp(pos, ios::cur);
file.write((char*)&ob, sizeof(ob));
}
}
file.close();
}
int main()
{
int sRollno;
//Store 4 records in file
for(int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
write_record();
//Display all records
cout << "\nList of records";
display();
//Search record
cout << "\nSearch result";
cin>>sRollno;
search(sRollno);
//Delete record
delete_record(sRollno);
cout << "\nRecord Deleted";
//Modify record
cout << "\nModify Record 101 ";
modify_record(101);
return 0;
}
Structure
Q1. What is a structure ?
Ans. A Structure is container for various type of data members which can be accessed by its structure variable.
Q2.what is the syntax for structure creation?
Ans.
Struct <structure_name >
{
Data_type data variable1;
data variable2;
data variable3;
} structure_variable;
Q3. How to access a structure member;
Ans.
Structure_variable . data_variable;
Q4. Wap to illustrate structure
Ans.
//structure
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Structure student
{
Int rollno;
Char name[30];
Float fee;
} s;
Void getdata(struct s )
{
Cout<<”\enter your rollno.:”;
Cin>>s.rollno;
Cout<<”\enter your name:”;
Cin>>s.name;
Cout<<”\enter your fee.:”;
Cin>>s.fee;
}
Void dispData(struct s )
{
Cout<<”\n Rollno is :”<<s.rollno;
Cout<<”\nName :”<<s.name;
Cout<<”\nFee : “<<s.fee;
Return;
}
void main()
{
Structure s;
getdata( s);
dispdata(s);
getch();
return;
}
UNION
Q1.What is a Union ?
A union is a used to access data variable with allocating space of highest datatype.
Q2.How to illustrate use of Union?
Ans.
Union register
{
Char ch=’A’;
Int num = 100;
Float amount=20.50;
Double reading = 200.002;
} u;
Void main()
{
Cout<<”\n Address of ch is :” <<&ch;
Cout<<”\n Address of num is “<<#
Cout<<”\n Address of amount is “<<&amount;
Cout<<”\n Address of reading is “<<&reading;
Getch();
Return;
}
C++ Project
Q1. Create a project on Employee Management System (EMS) with the following :
Tables
1. emptab
2. paytab
3. designtab
4. incrtab
5. depttab
6. RepTab
Data members